Object Detection Model: YOLOv5
This document demonstrates how to run the YOLOv5 object detection model on Allwinner T527/A733 series chips.
This example uses the pre-trained ONNX format model from ultralytics/yolov5 as an example to demonstrate the complete process of converting the model for inference on the board.
Deploying YOLOv5 on the board requires two steps:
- Use the ACUITY Toolkit on the PC to convert models from different frameworks into NBG format.
- Use the awnn API on the board to perform inference with the model.
Download the ai-sdk Example Repository
git clone https://github.com/ZIFENG278/ai-sdk.git
Model Conversion on PC
Radxa provides a pre-converted yolov5.nb model. Users can directly refer to YOLOv5 Inference on the Board and skip the PC model conversion section.
The files used in the YOLOv5 example are already included in the ai-sdk example repository under models/yolov5s-sim.
-
Enter the ACUITY Toolkit Docker container.
For ACUTIY Toolkit Docker environment preparation, please refer to ACUITY Toolkit Environment Configuration
Configure environment variables:
X86 Linux PCcd ai-sdk/models
source env.sh v3 # NPU_VERSIONFor A733, choose
v3; for T527, choosev2.tipRefer to the NPU Version Comparison Table for NPU version selection.
-
Download the YOLOv5s ONNX model.
X86 Linux PCmkdir yolov5s-sim && cd yolov5s-sim
wget https://github.com/ultralytics/yolov5/releases/download/v6.0/yolov5s.onnx -
Fix the input size.
NPU inference only accepts fixed input sizes. Use
onnxsimto fix the input size.X86 Linux PCpip3 install onnxsim onnxruntime
onnxsim yolov5s.onnx yolov5s-sim.onnx --overwrite-input-shape 1,3,640,640 -
Create a quantization calibration dataset.
Use a set of images for quantization calibration. Save the image paths in
dataset.txt.X86 Linux PCvim dataset.txtimages/COCO_train2014_000000000529.jpg
images/COCO_train2014_000000001183.jpg
images/COCO_train2014_000000002349.jpg
images/COCO_train2014_000000003685.jpg
images/COCO_train2014_000000004463.jpg
images/dog.jpg -
Create model input/output files.
Use Netron to confirm the input/output names of the ONNX model.
X86 Linux PCvim inputs_outputs.txt--inputs images --input-size-list '3,640,640' --outputs '350 498 646'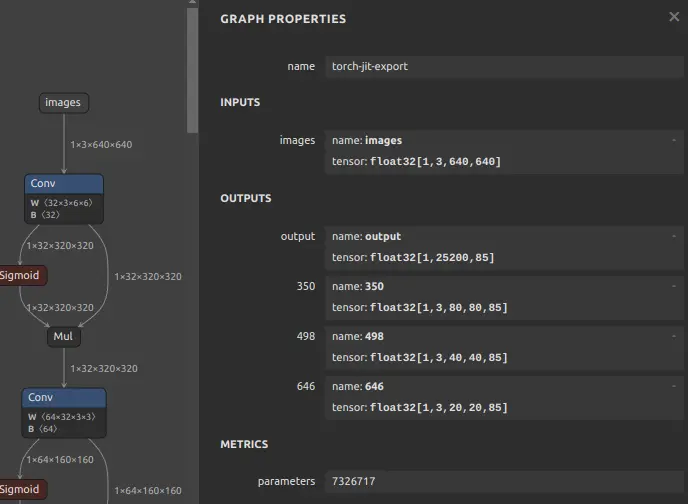
yolov5s in/output name
-
Directory structure:
.
|-- dataset.txt
|-- images
| |-- COCO_train2014_000000000529.jpg
| |-- COCO_train2014_000000001183.jpg
| |-- COCO_train2014_000000002349.jpg
| |-- COCO_train2014_000000003685.jpg
| |-- COCO_train2014_000000004463.jpg
| `-- dog.jpg
|-- inputs_outputs.txt
|-- yolov5s-sim.onnx -
Parse the model.
tipThe
pegasusscript is located inai-sdk/scriptsand can be copied to themodelsdirectory.Use
pegasus_import.shto parse the model into an intermediate representation (IR). This generatesyolov5s-sim.json(model structure) andyolov5s-sim.data(model weights).X86 Linux PC./pegasus_import.sh yolov5s-sim/ -
Modify the
yolov5s-sim_inputmeta.ymlfile.Update the
scalevalue based on the formulascale = 1 / std.scale = 1 / 255
scale = 0.00392157input_meta:
databases:
- path: dataset.txt
type: TEXT
ports:
- lid: images_208
category: image
dtype: float32
sparse: false
tensor_name:
layout: nchw
shape:
- 1
- 3
- 640
- 640
fitting: scale
preprocess:
reverse_channel: true
mean:
- 0
- 0
- 0
scale:
- 0.00392157
- 0.00392157
- 0.00392157
preproc_node_params:
add_preproc_node: false
preproc_type: IMAGE_RGB
# preproc_dtype_converter:
# quantizer: asymmetric_affine
# qtype: uint8
# scale: 1.0
# zero_point: 0
preproc_image_size:
- 640
- 640
preproc_crop:
enable_preproc_crop: false
crop_rect:
- 0
- 0
- 640
- 640
preproc_perm:
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
redirect_to_output: false -
Quantize the model.
Use
pegasus_quantize.shto quantize the model into uint8 format.X86 Linux PC./pegasus_quantize.sh yolov5s-sim/ uint8 10 -
Compile the model.
Use
pegasus_export_ovx.shto compile the model into NBG format.X86 Linux PC./pegasus_export_ovx.sh yolov5s-sim/ uint8The NBG model is saved in
yolov5s-sim/wksp/yolov5s-sim_uint8_nbg_unify/network_binary.nb.
YOLOv5 Inference on the Board
Navigate to the YOLOv5 example code directory.
cd ai-sdk/examples/yolov5
Compile the Example
make AI_SDK_PLATFORM=a733
make install AI_SDK_PLATFORM=a733 INSTALL_PREFIX=./
Parameter explanation:
AI_SDK_PLATFORM: Specify the SoC, options area733,t527.INSTALL_PREFIX: Specify the installation path.
Run the Example
Set environment variables.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/home/rock/ai-sdk/viplite-tina/lib/aarch64-none-linux-gnu/NPU_VERSION # NPU_SW_VERSION
Specify NPU_SW_VERSION. For A733, choose v2.0; for T527, choose v1.13. Refer to the NPU Version Comparison Table for details.
Navigate to the example installation directory.
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/home/rock/ai-sdk/viplite-tina/lib/aarch64-none-linux-gnu/NPU_VERSION # NPU_SW_VERSION
cd INSTALL_PREFIX/etc/npu/yolov5
# ./yolov5 nbg_model input_picture
./yolov5 ./model/yolov5.nb ./input_data/dog.jpg
The example automatically installs the yolov5.nb model provided by Radxa. You can manually specify the path to your converted NBG model.
(.venv) rock@radxa-cubie-a7a:~/ai-sdk/examples/yolov5/etc/npu/yolov5$ ./yolov5 ./model/network_binary.nb ./input_data/dog.jpg
./yolov5 nbg input
VIPLite driver software version 2.0.3.2-AW-2024-08-30
viplite init OK.
VIPLite driver version=0x00020003...
VIP cid=0x1000003b, device_count=1
* device[0] core_count=1
awnn_init total: 5.49 ms.
vip_create_network ./model/network_binary.nb: 3.96 ms.
input 0 dim 640 640 3 1, data_format=2, name=input/output[0], elements=1833508979, scale=0.003922, zero_point=0
create input buffer 0: 1228800
output 0 dim 85 80 80 3 1, data_format=2, name=uid_5_out_0, elements=1632000, scale=0.085919, zero_point=211
create output buffer 0: 1632000
output 1 dim 85 40 40 3 1, data_format=2, name=uid_4_out_0, elements=408000, scale=0.071616, zero_point=204
create output buffer 1: 408000
output 2 dim 85 20 20 3 1, data_format=2, name=uid_3_out_0, elements=102000, scale=0.072006, zero_point=196
create output buffer 2: 102000
memory pool size=3892224 bytes
load_param ./model/network_binary.nb: 0.97 ms.
prepare network ./model/network_binary.nb: 2.56 ms.
set network io ./model/network_binary.nb: 0.01 ms.
awnn_create total: 7.55 ms.
yolov5_preprocess.cpp run.
memcpy(0xffff89621000, 0xffff886f8010, 1228800) load_input_data: 0.33 ms.
vip_flush_buffer input: 0.02 ms.
awnn_set_input_buffers total: 0.38 ms.
vip_run_network: 17.07 ms.
vip_flush_buffer output: 0.01 ms.
int8/uint8 1632000 memcpy: 2.72 ms.
int8/uint8 408000 memcpy: 0.46 ms.
int8/uint8 102000 memcpy: 0.11 ms.
tensor to fp: 28.64 ms.
awnn_run total: 45.75 ms.
yolov5_postprocess.cpp run.
detection num: 3
16: 86%, [ 130, 222, 312, 546], dog
7: 59%, [ 469, 78, 692, 171], truck
1: 53%, [ 158, 133, 560, 424], bicycle
awnn_destroy total: 1.95 ms.
awnn_uninit total: 0.66 ms.
The inference result is saved in result.png.
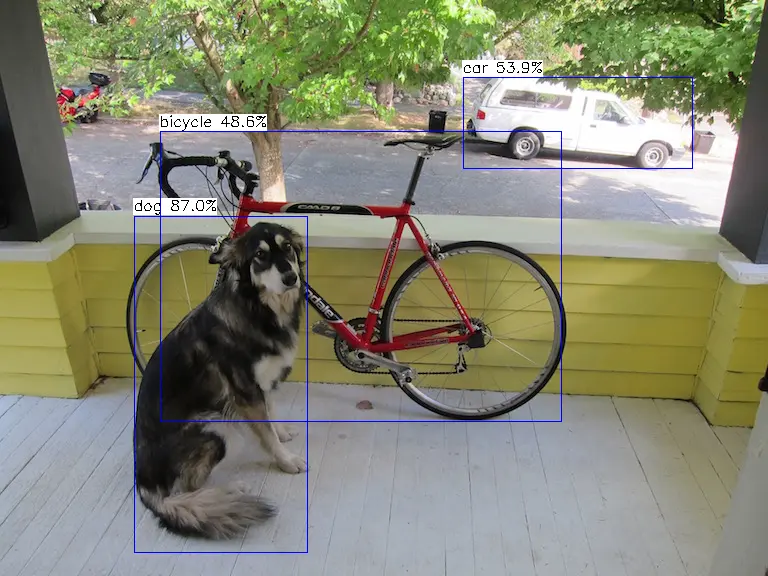
YOLOv5s demo output