SSH Remote Access
Prerequisites
For SSH remote access, both devices must be on the same Local Area Network (LAN), and the target device must have the SSH service enabled.
The system images we provide have the SSH service enabled by default, allowing for direct SSH remote control. If it is not installed or enabled, you can follow the instructions below to set it up!
Install OpenSSH
SSH remote control requires the installation of OpenSSH. Run the following command in the device's terminal to install it:
sudo apt update && sudo apt install openssh-server -y
Start the SSH Service
Run the following command in the device's terminal to start the SSH service:
sudo systemctl start ssh
Enable SSH Service to Start on Boot
Run the following command in the device's terminal to configure the SSH service to start automatically on boot:
sudo systemctl enable ssh
Check the SSH Service Status
Run the following command in the device's terminal to check the status of the SSH service:
sudo systemctl status ssh
The terminal will output information similar to the following: Prompt you whether the SSH service is autostarted and its current running status.
● ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ssh.service; enabled; vendor preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Sat 2000-01-01 00:14:50 UTC; 25 years 5 months ago
Docs: man:sshd(8)
man:sshd_config(5)
Main PID: 518 (sshd)
CPU: 284ms
CGroup: /system.slice/ssh.service
└─518 sshd: /usr/sbin/sshd -D [listener] 0 of 10-100 startups
Remote Control via SSH
You can log in remotely via SSH using the terminal command line or Tabby software.
- terminal command line
- Using Tabby Software
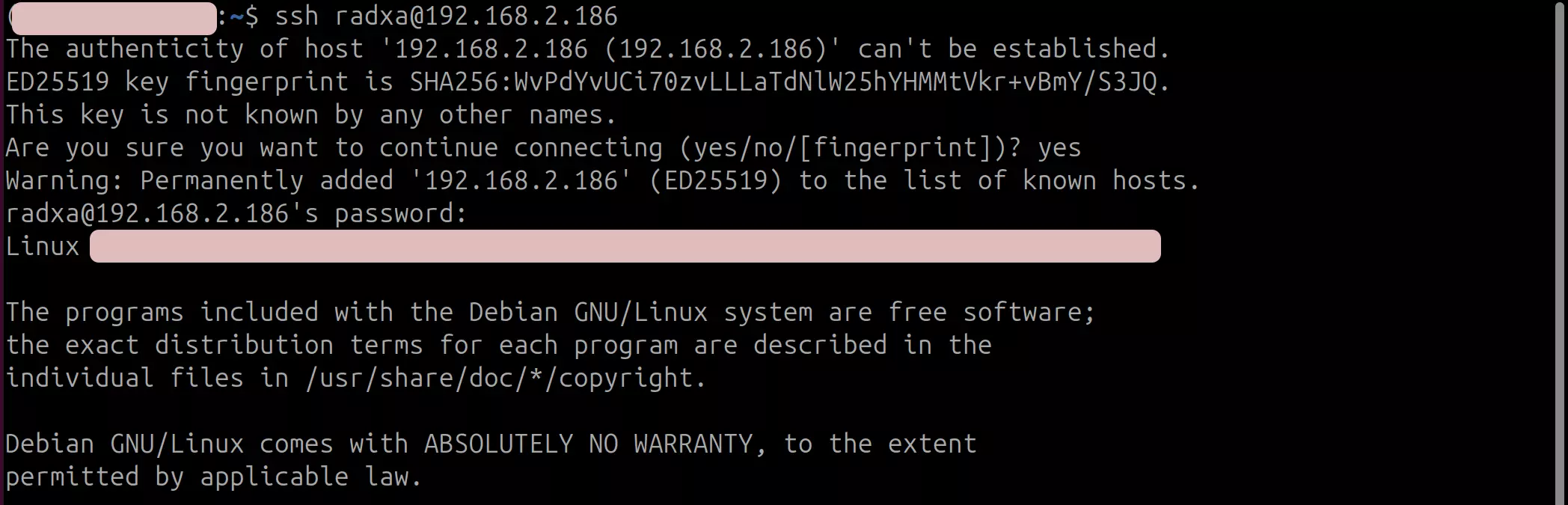
Open a terminal on another device and enter the following command to log in remotely:
ssh <user-name>@<ip-address>
# Example
ssh [email protected]
In this case, <user-name> and <ip-address> are the actual username and IP address of the target device, respectively.
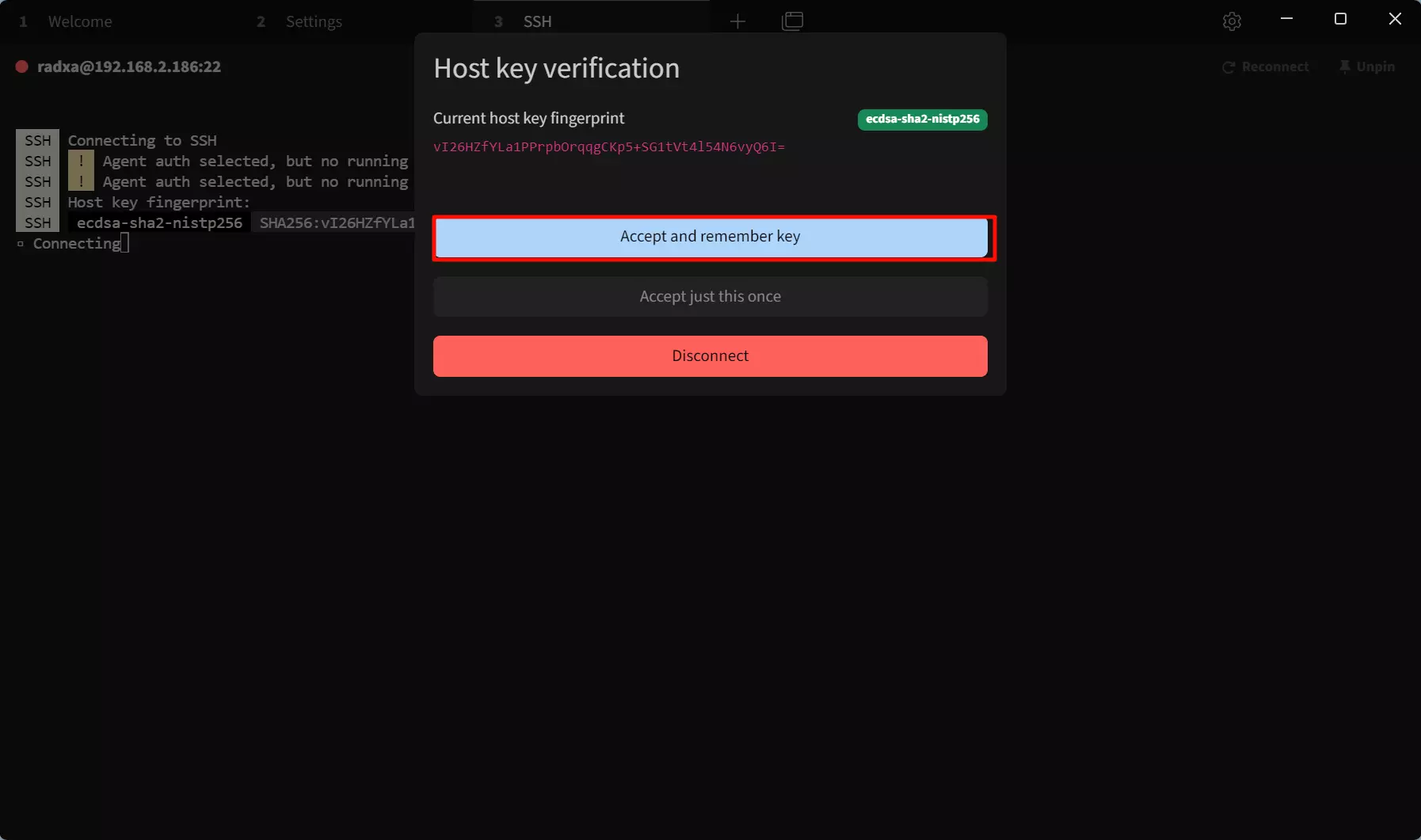
During the connection process, you will need to enter “yes” to confirm the connection.
Tabby is a powerful cross-platform serial port debugging tool that supports multiple protocols such as serial ports and SSH. We recommend using Tabby software for SSH remote login.
Tabby Download
Visit the Tabby official website (https://tabby.sh/) to download and install the Tabby software.
Tabby Installation
-
Windows
-
Linux
Select the .exe file for installation based on your system architecture.
- MacOS
Select the .dmg file for installation based on your system architecture.
Tabby Usage
Double-click the Tabby software icon to open the Tabby software.
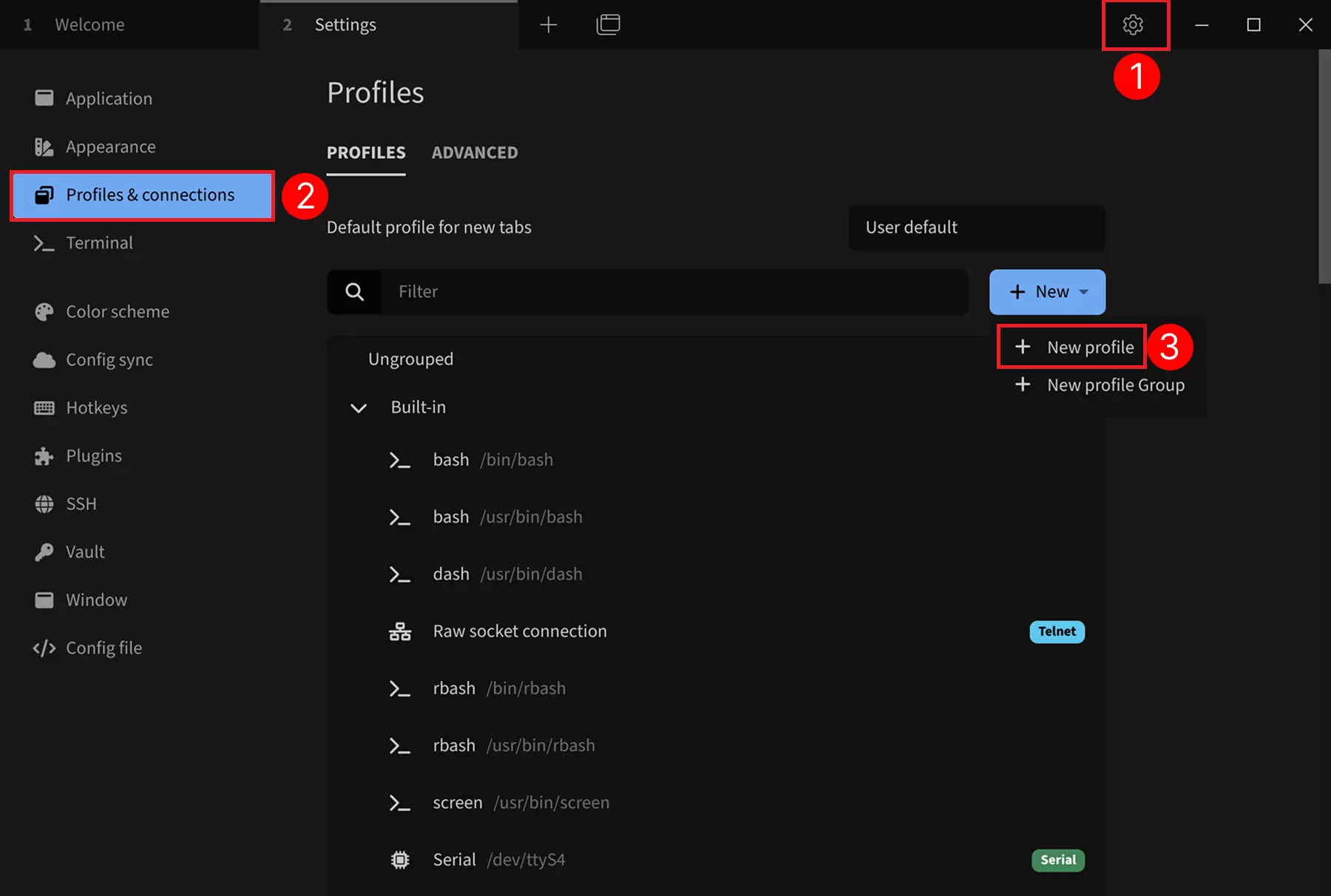
SSH Configuration
① --> Settings : Click the Settings option.
② --> Profiles & connections : Click Configure Connection Options
③ --> New profile : Click to add a new configuration option.
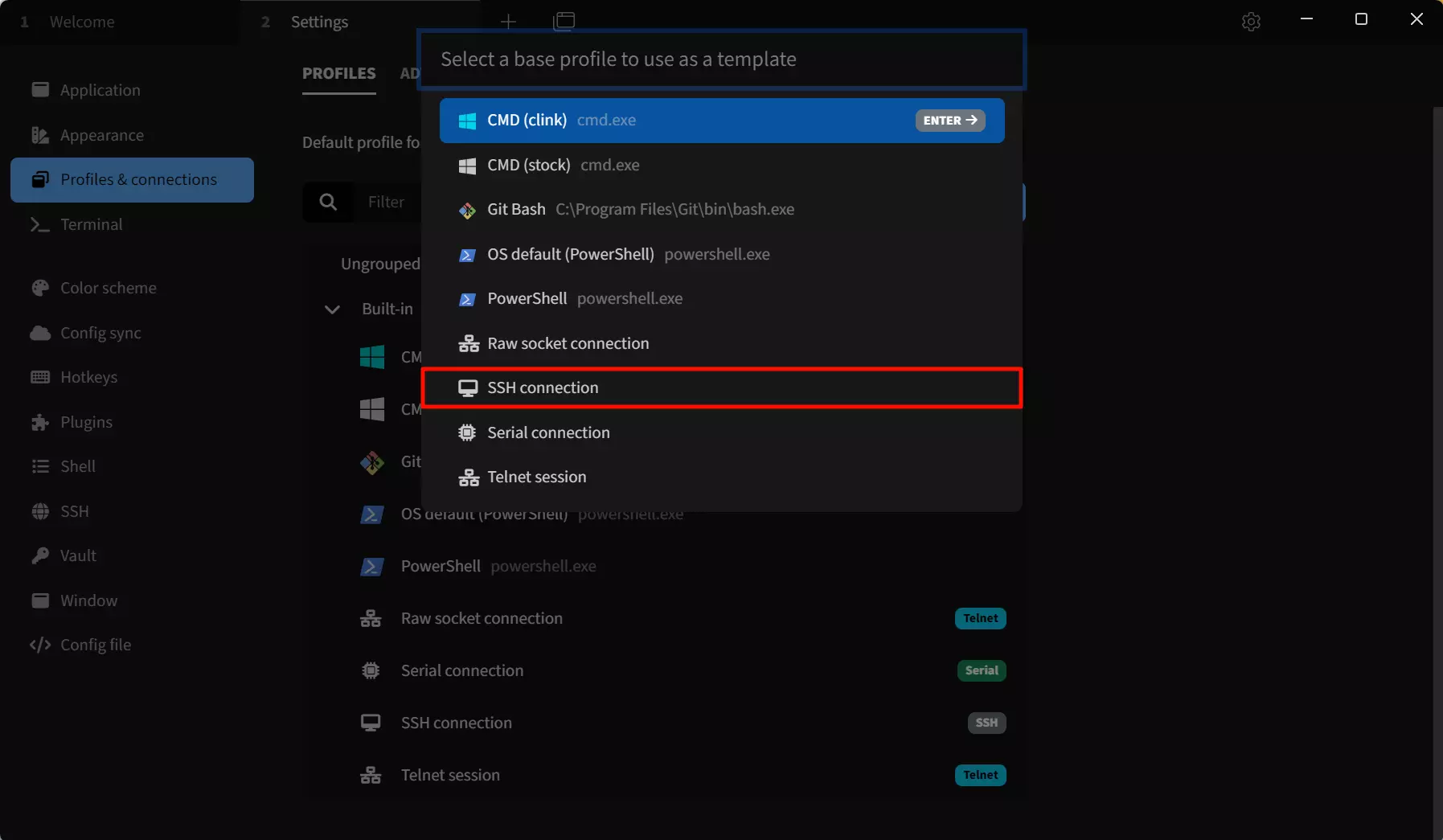
Select SSH Template
Select a basic configuration as a template: Select the SSH connection template, and we can modify parameters such as device name, IP address, and port in the subsequent configuration interface.
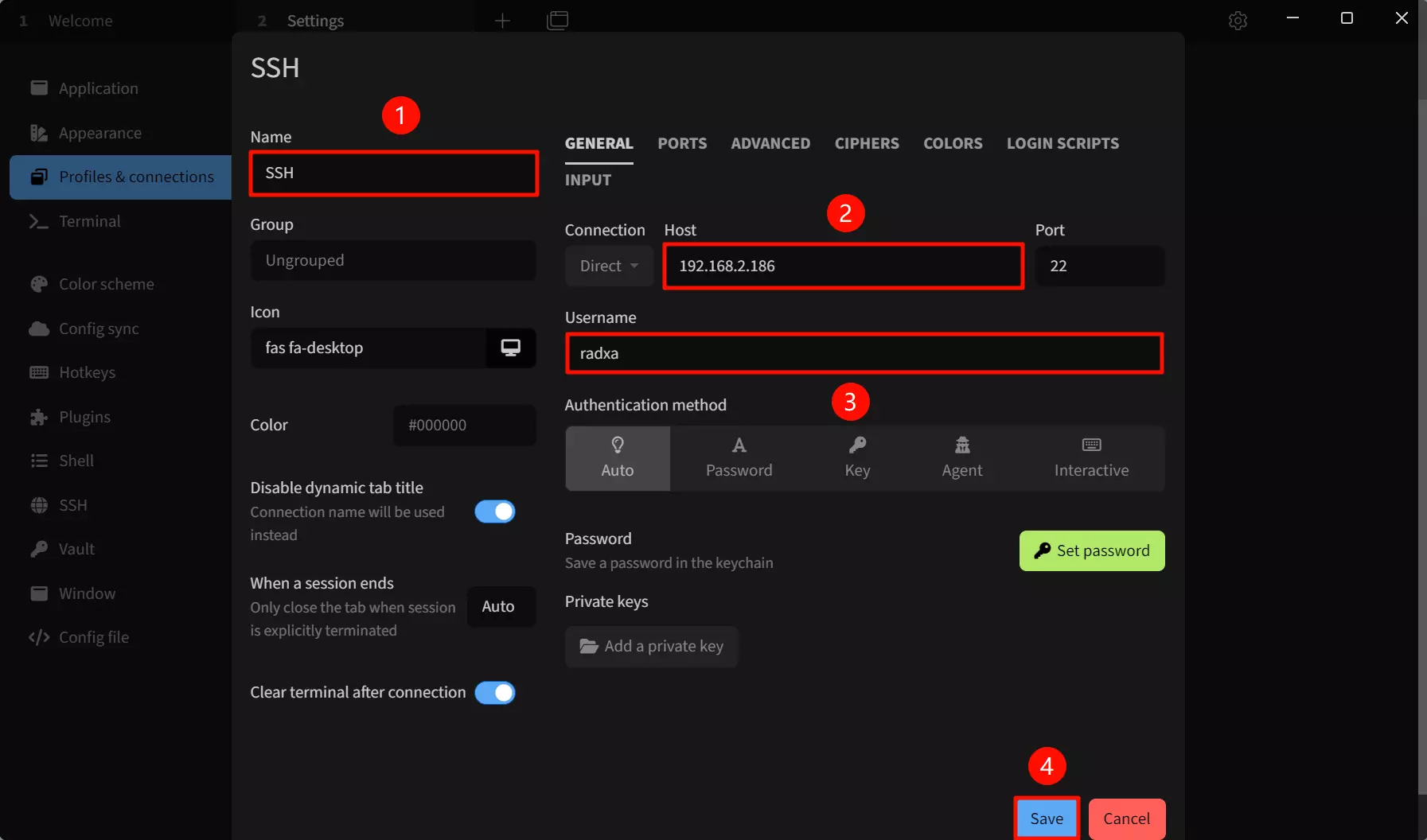
After selecting the SSH connection template, modify the following parameters:
① --> Name : Set connection name
② --> Host : Set the IP address according to the actual IP address of the target device.
③ --> User : Set the username. The default factory username is radxa.
④ --> Save : Save configuration
The default port number is 22, so no modification is necessary.
Run SSH connection
Click the Run button to connect remotely to the SSH device.
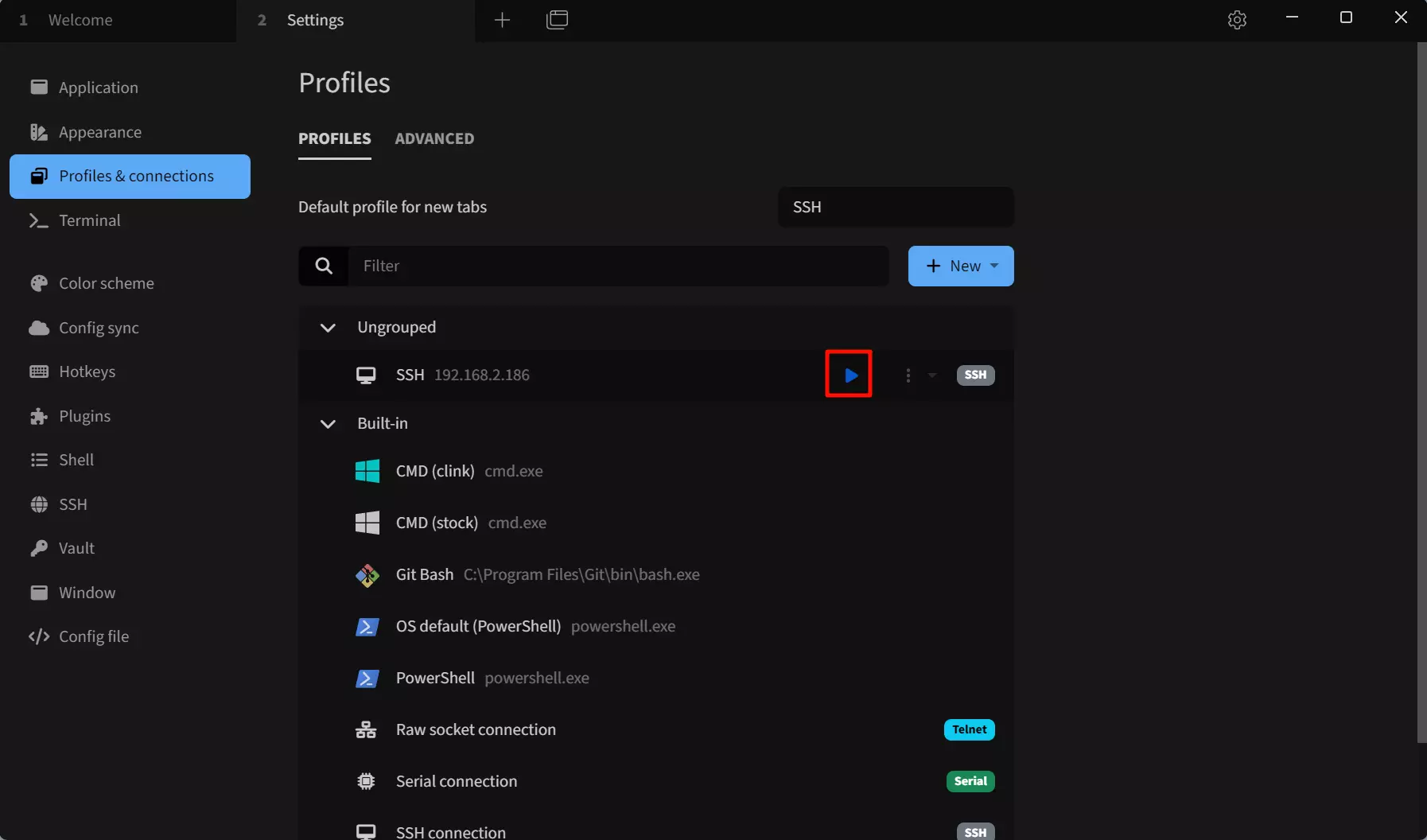
Click the Run button to connect remotely to the SSH device.
① --> password : Enter the password for the target device.
② --> OK : Confirm connection
We recommend checking the “Remember” option so that you don't have to enter your password the next time you connect.
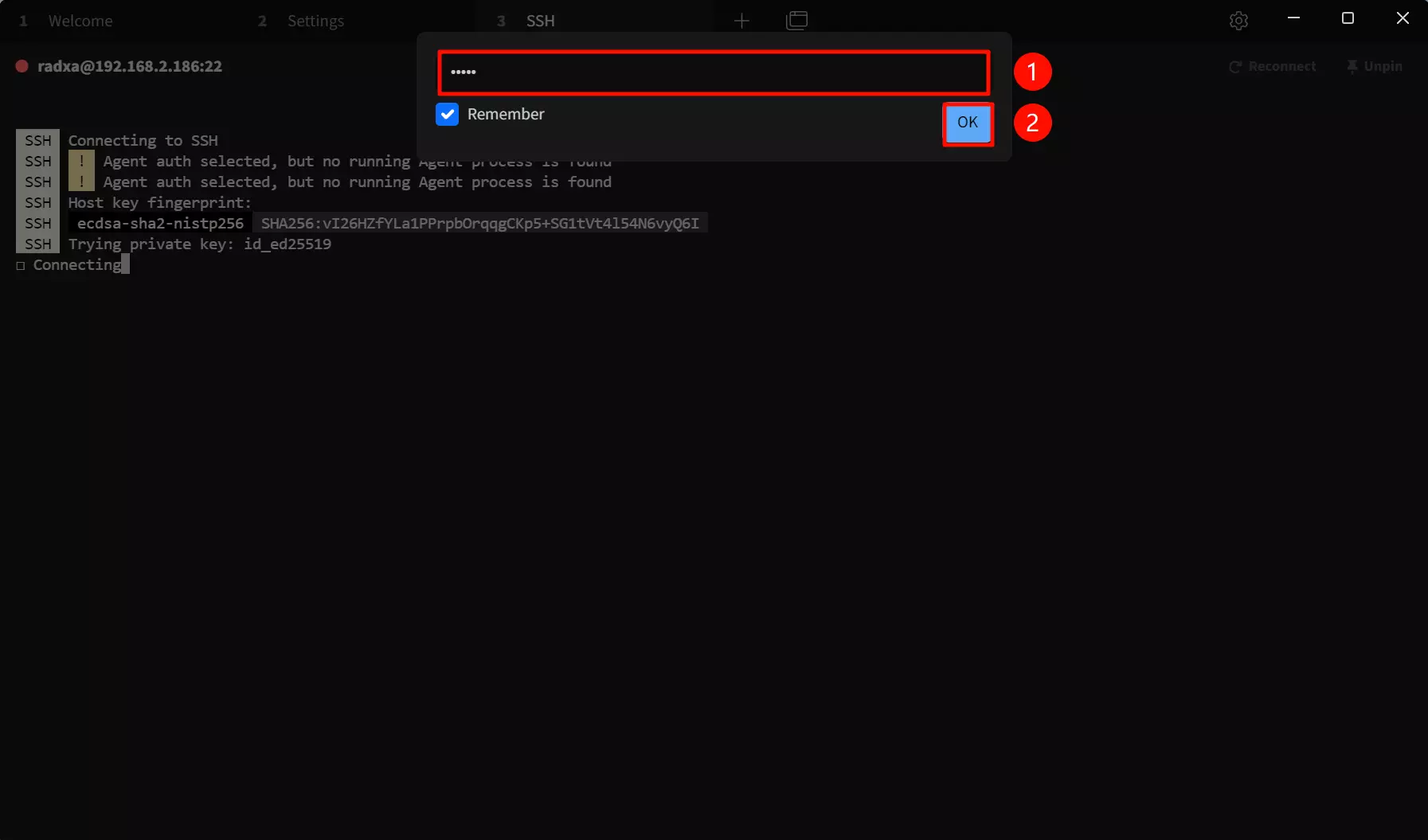
After the connection is successful, the remote interface will appear.
After successfully logging in remotely via SSH, you can run commands to control the system via SSH.