Buildroot Build
Environment Preparation
You need to prepare an Ubuntu 20.04/22.04 x86_64 host machine.
You can also use a virtual machine
- ubuntu-22.04.5-live-server-amd64 virtual machine with at least 120GB of available disk space.
Install Build Dependencies
sudo apt update
sudo apt install python2 git rsync gcc g++ make device-tree-compiler bc flex bison lz4 libssl-dev libgmp-dev libmpc-dev expect expect-dev file unzip bzip2 fakeroot bsdmainutils
sudo ln -s /bin/python2 /bin/python
Download Rockchip Original SDK
Extract the SDK
On your Ubuntu PC, use the following commands to extract the SDK.
tar xvf rk3576_linux6.1_rkr4_sdk.repo.tar
.repo/repo/repo sync -l
Add ROCK 4D Board Support
Use the rockchip repository maintained by Radxa.
cd device/rockchip
git remote add radxa https://github.com/radxa/device-rockchip.git
git fetch radxa
git checkout -b rk3576-linux-6.1 remotes/radxa/rk3576-linux-6.1
Use the kernel repository maintained by Radxa.
cd kernel
git remote add radxa https://github.com/radxa/kernel.git
git fetch radxa
git checkout -b linux-6.1-stan-rkr4.1-buildroot remotes/radxa/linux-6.1-stan-rkr4.1-buildroot
Use the rkwifibt repository maintained by Radxa.
cd external/rkwifibt
git remote add radxa https://github.com/radxa/rkwifibt.git
git fetch radxa
git checkout -b develop remotes/radxa/develop
Use the buildroot repository maintained by Radxa.
cd buildroot
git remote add radxa https://github.com/radxa/buildroot.git
git fetch radxa
git checkout -b rockchip/2024.02 remotes/radxa/rockchip/2024.02
Build the SDK
In the top-level directory of the SDK, execute the command:
./build.sh
Then select the configuration file rockchip_rk3576_rock_4d_defconfig.
After the build is complete, the image will be generated in the rockdev/ directory. The system image file is update.img.
Flashing the Image
Flash Image to UFS/EMMC
On a Linux/Mac OS host, use the upgrade_tool to flash the system image update.img to UFS/EMMC through the Type-A port.
upgrade_tool uf update.img
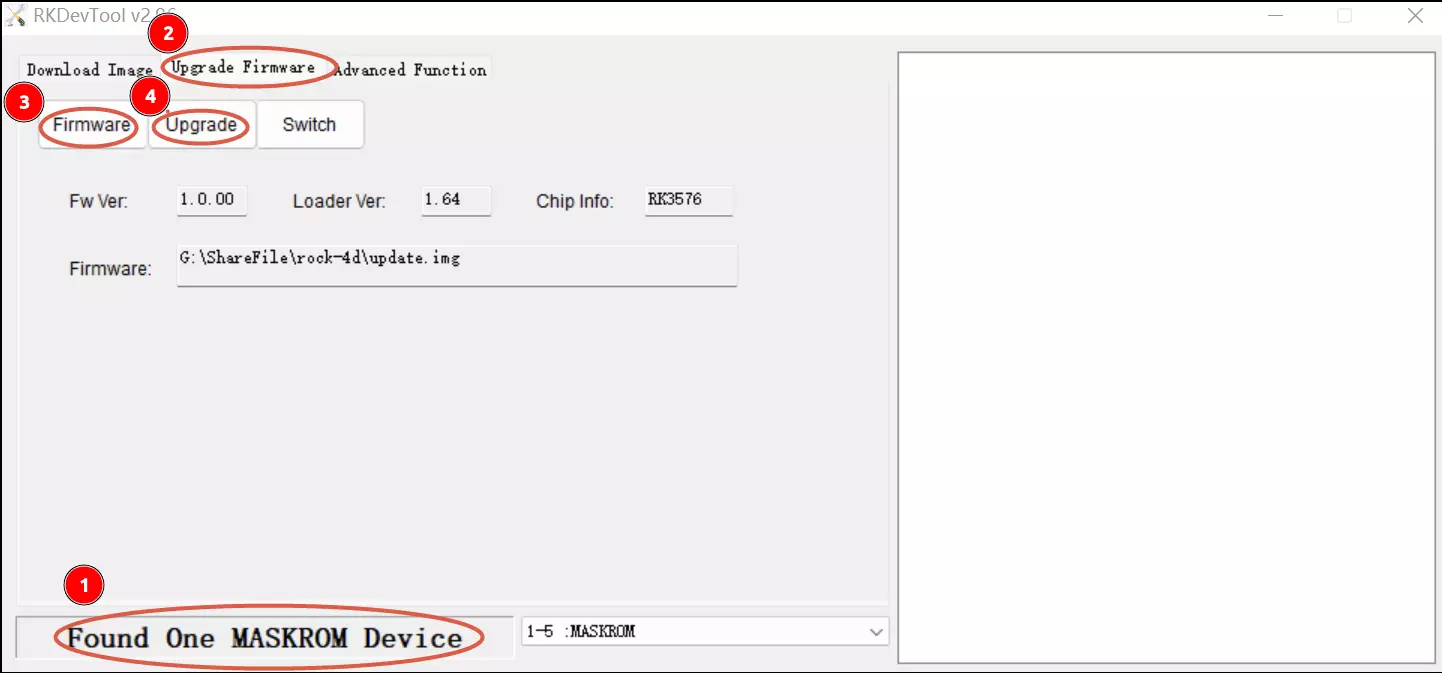
On a Windows host, use the RKDevTool to flash the system image update.img to UFS/EMMC through the Type-A port.
-
①: Put the device into Maskrom mode
-
②: Select the
Upgrade Firmwareoption -
③: Click the
Firmwareoption and select your compiledupdate.img -
④: Click the
Upgradebutton to start flashing the system image
Flash Image to MicroSD Card
Use SDDiskTool to flash the generated image to a MicroSD Card.
SDDiskTool is Rockchip's official SD card flashing tool.
-
Download SDDiskTool
-
SDDiskTool currently only has a Windows version, so please use it on a Windows computer.
-
Download link:SDDiskTool_en_v1.74.zip
-
-
Flash SD card
-
We need to flash the corresponding complete image in RK format.
-
Complete image in RK format refers to The
update.imgimage compiled using a series of Linux SDKs released by Rockchip based on Buildroot -
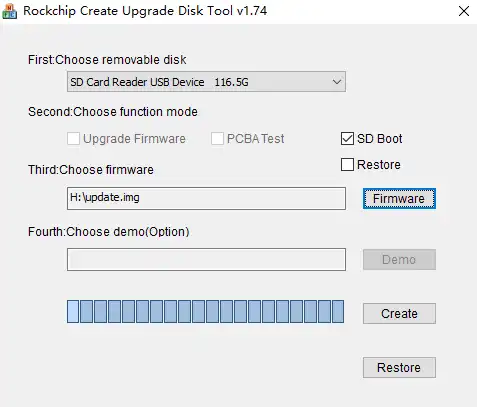
Open the executable file
SD_Firmware_Tool.exeof SDDiskTool and insert the SD card.warningWhen multiple storage devices are connected, please ensure you select the correct SD card to flash, otherwise other storage devices may be overwritten.
-
Select the SD card to flash from the removable disk devices, choose SD Boot as the function mode, ensure that the firmware upgrade is a complete image in RK format, and finally click Create to flash the image.
-
Please be patient during the flashing process. The image contains many partitions, and if the image is large, the flashing time will be longer.
-
If you encounter problems clearing the MBR while burning, you need to change the SD card disk label type from dos to gpt.
- Windows
- Linux
-
Delete all partitions and convert to gpt using command prompt under windows
-
Press Win + X and select Windows Terminal (Administrator) or Command Prompt (Administrator).
-
Enter the following command and press Enter:
Host-Windows$diskpart -
Then, enter the following command to list all disks:
Host-Windows$list disk -
Locate your SD card (assuming it is disk 3) and enter:
Host-Windows$select disk 3- (If your SD card has a different disk number, change 3 to the correct number accordingly.)
-
Clear all partitions on the disk:
Host-Windows$clean- (This deletes all partitions and data on the SD card.)
-
Converts a disk to GPT format:
Host-Windows$convert gpt -
Type
exitto exit the diskpart utility.
-
-
Use the fdisk command to change the label format to gpt on Linux.
-
Find your SD card (assuming it's /dev/sdb) and enter:
Host-Linux$sudo fdisk /dev/sdb -
Type
pand the label format and partition of the current disk will be displayed. -
Then type
gto convert the disk to gpt format -
Then just type
wqto save and exit.
-