YOLOv4 Object Detection
This document explains in detail how to utilize NPU hardware acceleration on the Sirider S1 to infer the YOLOv4 model.
The document is divided into two parts: Quick Start and Detailed Tutorial.
Quick Start
Radxa provides a ready-to-use YOLOv4 object detection example, allowing users to run the yolov4_tiny model on the Sirider S1 using AIPU for inference. This eliminates the need for complex model compilation and execution code setup, making it an ideal choice for those who want to quickly use AIPU without building models from scratch. For those interested in the full workflow, refer to the Detailed Tutorial section.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/zifeng-radxa/siriders1_NPU_yolov4_tiny_demo.git -
Install dependencies:
tipIt is recommended to use
virtualenv.cd siriders1_NPU_yolov4_tiny_demo/demo
pip3 install -r requirements.txt -
Run the YOLOv4 demo program:
python3 yolov4_aipu.py -m [mode] -i [your_input_path] -r
# Example: python3 yolov4_aipu.py -m camera -rParameter details:
-h,--help: Print parameter information.-m,--mode: Select input mode, supports ['camera', 'video', 'image'].-i,--input: Input file path, required when mode is ['video', 'image'].-r,--real_time: Real-time preview.-s,--save: Save the output to theoutputfolder.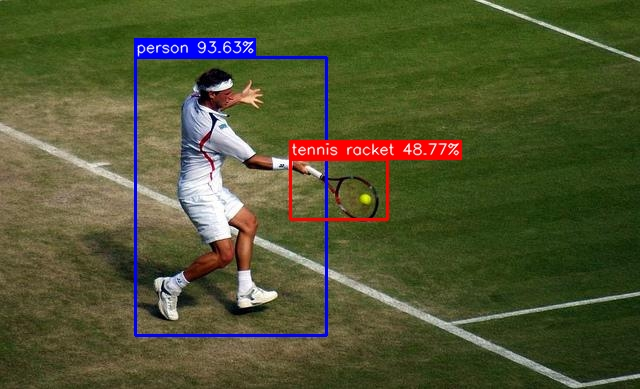
Detailed Tutorial
To deploy the target model on the Zhouyi Z2, there are three main steps: model conversion, compiling the inference file, and application-level programming.
Model Conversion
This step is completed on an x86 host. Before starting model conversion, install the Zhouyi SDK according to the Zhouyi AIPU SDK Installation Guide and complete the Configure the nn-compiler Environment.
-
Clone the repository:
git clone https://github.com/zifeng-radxa/siriders1_NPU_yolov4_tiny_demo.git -
Generate quantization data:
cd siriders1_NPU_yolov4_tiny_demo/convert
python3 preprocess.py -
Generate the AIPU model:
aipubuild tflite_yolo_v4_tinybuild.cfgtipIf the
aipubuildcommand is not found, try adding it to your path:export PATH=$PATH:/root/.local/binThe target model is generated at
./aipu_yolov4_tiny.bin.
Compile AIPU Executable Inference File
Compile an executable file for inferring the Zhouyi Z2 AIPU model.
-
Copy the
compilefolder from the repository to the Zhouyi SDK.Copy the
compilefolder from thesiriders1_NPU_yolov4_tiny_demorepository toYOUR_SDK_PATH/siengine. Make sure to replace YOUR_SDK_PATH with your actual path.cp -r compile YOUR_SDK_PATH/siengine -
Cross-compile:
tipModify the
Linux_Tool_ROOTinCMakeLists.txtto match your cross-compilation toolchain path. The default path is/opt/gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu/bin.Download the cross-compilation toolchain: gcc-linaro-7.5.0-2019.12-x86_64_aarch64-linux-gnu.
cd YOUR_SDK_PATH/siengine/compile
mkdir build && cd build
cmake -DCMAKE_BUILD_TYPE=Release .. && make
cd ..The output files are located in the
outfolder.
Testing on the Board
Transfer the generated aipu_yolov4_tiny.bin model file and the files under out/linux to the Sirider S1.
Use yolov4_aipu.py to test the results:
export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:linux/libs
python3 yolov4_aipu.py -m image -i YOUR_IMAGE_PATH -r