在 Linux 下控制 RP2040
概述
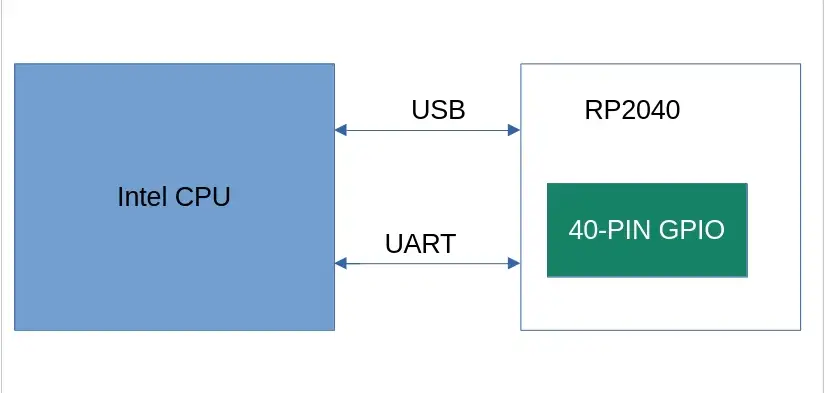
在 Radxa X4 上集成了 一块 Intel N100 的 CPU 和 一块 RP2040 MCU,两者通过 USB 或 UART 进行通信。 40-PIN 是从 RP2040 拉出来的 IO 扩展口,CPU 通过与 RP2040 通信来控制 40-PIN. 其中 RP2040 通过 PICO SDK 来操作 40-PIN。
工具介绍
为了操作 RP2040 上的 IO 资源, 我们需要一套完善的软件环境,在这里我们主要介绍一套 C/C++ SDK,即 pico-sdk 和 pico-example。 pico-sdk 主要是提供了一些操作 RP2040 的 API, 而 pico-examples 则为我们提供了一套程序编译框架,我们可以根据 pico-examples 提供的编译框架来添加我们自己的程序。
PICO-SDK
-
简介
Pico SDK(以下简称 SDK)提供了使用 C、C++ 或汇编语言为基于 RP2040 的设备(如 Raspberry Pi Pico/Radxa X4)编写程序所需的标头、库和构建系统。
SDK 旨在提供非嵌入式 C 开发人员和嵌入式 C 开发人员都熟悉的 API 和编程环境。单个程序一次在设备上运行,并以常规方法启动main()。 支持标准 C/C++ 库以及用于访问 RP2040 的所有硬件(包括 PIO(可编程 IO))的 C 级库/API。
-
使用
既可以在 PC 端的 Linux 环境中下载 pico-sdk/pico-examples 以及安装相应工具,也可以在 Radxa X4 的 Linux 环境下。为方便起见,我们可以直接在 Radxa X4 的 Linux 环境中进行操作。
- 安装必要工具
sudo apt update -y
sudo apt install -y git cmake gcc-arm-none-eabi libnewlib-arm-none-eabi libstdc++-arm-none-eabi-newlib
- 获取代码
git clone https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-sdk.git
cd pico-sdk
git submodule update --init
PICO-EXAMPLES
-
简介
pico-examples 是一个官方示例代码库,展示了如何使用 Raspberry Pi Pico 和 Pico SDK 来实现各种功能。 它提供了一系列的示例,涵盖了从基本 GPIO 操作到复杂的通信协议,使开发者能够快速上手并理解如何在 Pico 上进行开发。
-
使用
既可以在 PC 端的 Linux 环境中下载 pico-sdk/pico-examples 以及安装相应工具,也可以在 Radxa X4 的 Linux 环境下。为方便起见,我们可以直接在 Radxa X4 的 Linux 环境中进行操作。
- 获取代码
git clone https://github.com/raspberrypi/pico-examples.git --branch master
- 编译
export PICO_SDK_PATH=path/to/pico-sdk
cd pico-examples
mkdir build
cd build
cmake .. && make -j4
示例
RP2040 控制 40-PIN
- GPIO
- I2C
- MCP2515
- PWM
- PoE FAN
- UART
GPIO
1. 准备
- 一块 Radxa X4
- 一个 LED
2. 连接
| Radxa X4 | <--> | LED |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_5 | <--> | LED |
| PIN_1 | <--> | VCC |
| PIN_9 | <--> | GND |
这里的 PIN_5 对应 下面代码中的 GPIO29, 详细请参考 GPIO 定义
3. 测试
-
将以下代码替换 pico-examples/blink/blink.c
blink.c
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#define BLINK_PIN 29 // GPIO29
int main() {
gpio_init(BLINK_PIN);
gpio_set_dir(BLINK_PIN, GPIO_OUT);
while (true) {
gpio_put(BLINK_PIN, 1);
sleep_ms(250);
gpio_put(BLINK_PIN, 0);
sleep_ms(250);
}
} -
编译
成功编译后,在 pico-examples/build/blink/ 目录下会产生一个名为 blink.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
- 重启 RP2040
-
将 blink.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失后, LED 会开始闪烁
I2C
1. 准备
- 一块 Radxa X4
- 一个 I2C OLED 1306
2. 连接
| Radxa X4 | <--> | OLED |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_5 | <--> | SCL |
| PIN_3 | <--> | SDA |
| PIN_1 | <--> | VCC |
| PIN_9 | <--> | GND |
这里的 PIN_5 对应 下面代码中的 GPIO29 的复用属性 I2C0 SDA, PIN_3 对应 下面代码中的 GPIO28 的复用属性 I2C0 SCL, 详细请参考 GPIO 定义
3. 测试
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/i2c/lcd_1602_i2c/lcd_1602_i2c.c
lcd_1602_i2c.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/i2c.h"
#include "pico/binary_info.h"
#define I2C_ID i2c0
#define I2C_SDA_PIN 28
#define I2C_SCL_PIN 29
// commands
const int LCD_CLEARDISPLAY = 0x01;
const int LCD_RETURNHOME = 0x02;
const int LCD_ENTRYMODESET = 0x04;
const int LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL = 0x08;
const int LCD_CURSORSHIFT = 0x10;
const int LCD_FUNCTIONSET = 0x20;
const int LCD_SETCGRAMADDR = 0x40;
const int LCD_SETDDRAMADDR = 0x80;
// flags for display entry mode
const int LCD_ENTRYSHIFTINCREMENT = 0x01;
const int LCD_ENTRYLEFT = 0x02;
// flags for display and cursor control
const int LCD_BLINKON = 0x01;
const int LCD_CURSORON = 0x02;
const int LCD_DISPLAYON = 0x04;
// flags for display and cursor shift
const int LCD_MOVERIGHT = 0x04;
const int LCD_DISPLAYMOVE = 0x08;
// flags for function set
const int LCD_5x10DOTS = 0x04;
const int LCD_2LINE = 0x08;
const int LCD_8BITMODE = 0x10;
// flag for backlight control
const int LCD_BACKLIGHT = 0x08;
const int LCD_ENABLE_BIT = 0x04;
// By default these LCD display drivers are on bus address 0x27
static int addr = 0x27;
// Modes for lcd_send_byte
#define LCD_CHARACTER 1
#define LCD_COMMAND 0
#define MAX_LINES 2
#define MAX_CHARS 16
/* Quick helper function for single byte transfers */
void i2c_write_byte(uint8_t val) {
i2c_write_blocking(I2C_ID, addr, &val, 1, false);
}
void lcd_toggle_enable(uint8_t val) {
// Toggle enable pin on LCD display
// We cannot do this too quickly or things don't work
#define DELAY_US 600
sleep_us(DELAY_US);
i2c_write_byte(val | LCD_ENABLE_BIT);
sleep_us(DELAY_US);
i2c_write_byte(val & ~LCD_ENABLE_BIT);
sleep_us(DELAY_US);
}
// The display is sent a byte as two separate nibble transfers
void lcd_send_byte(uint8_t val, int mode) {
uint8_t high = mode | (val & 0xF0) | LCD_BACKLIGHT;
uint8_t low = mode | ((val << 4) & 0xF0) | LCD_BACKLIGHT;
i2c_write_byte(high);
lcd_toggle_enable(high);
i2c_write_byte(low);
lcd_toggle_enable(low);
}
void lcd_clear(void) {
lcd_send_byte(LCD_CLEARDISPLAY, LCD_COMMAND);
}
// go to location on LCD
void lcd_set_cursor(int line, int position) {
int val = (line == 0) ? 0x80 + position : 0xC0 + position;
lcd_send_byte(val, LCD_COMMAND);
}
static void inline lcd_char(char val) {
lcd_send_byte(val, LCD_CHARACTER);
}
void lcd_string(const char *s) {
while (*s) {
lcd_char(*s++);
}
}
void lcd- _init() {
lcd_send_byte(0x03, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_send_byte(0x03, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_send_byte(0x03, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_send_byte(0x02, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_send_byte(LCD_ENTRYMODESET | LCD_ENTRYLEFT, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_send_byte(LCD_FUNCTIONSET | LCD_2LINE, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_send_byte(LCD_DISPLAYCONTROL | LCD_DISPLAYON, LCD_COMMAND);
lcd_clear();
}
int main() {
i2c_init(I2C_ID, 100 * 1000);
gpio_set_function(I2C_SDA_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_I2C);
gpio_set_function(I2C_SCL_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_I2C);
gpio_pull_up(I2C_SDA_PIN);
gpio_pull_up(I2C_SCL_PIN);
// Make the I2C pins available to picotool
bi_decl(bi_2pins_with_func(I2C_SDA_PIN, I2C_SCL_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_I2C));
lcd_init();
static char *message[] =
{
"RP2040 by", "Raspberry Pi",
"A brand new", "microcontroller",
"Twin core M0", "Full C SDK",
"More power in", "your product",
"More beans", "than Heinz!"
};
while (1) {
for (int m = 0; m < sizeof(message) / sizeof(message[0]); m += MAX_LINES) {
for (int line = 0; line < MAX_LINES; line++) {
lcd_set_cursor(line, (MAX_CHARS / 2) - strlen(message[m + line]) / 2);
lcd_string(message[m + line]);
}
sleep_ms(2000);
lcd_clear();
}
}
}
-
编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
成功编译后,在 pico-examples/build/i2c/lcd_1602_i2c/ 目录下会产生一个名为 lcd_1602_i2c.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
- 重启 RP2040
-
将 lcd_1602_i2c.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失后, OLED 会一段文本
MCP2515
-
准备
-
一块 Radxa X4
-
一个 MCP2515 模块
-
连接
| Radxa X4 | <--> | MCP2515 |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_13 | <--> | SPI SCK |
| PIN_11 | <--> | SPI CS |
| PIN_15 | <--> | SPI TX |
| PIN_7 | <--> | SPI RX |
| PIN_1 | <--> | VCC |
| PIN_9 | <--> | GND |
以下程序仅用于回环测试,所以需要短接 MCP2515 的 PIN_H 和 PIN_L
- 下载 MCP2515 的库
cd pico-examples
git clone https://github.com/adamczykpiotr/pico-mcp2515.git
- 将 pico-mcp2515 添加到 pico-examples 的编译
编辑 pico-examples/CMakeLists.txt
... ...
add_subdirectory(pico_w)
add_subdirectory(pico-mcp2515)
add_subdirectory(pio)
... ...
- 打开串口
编辑 pico-examples/pico-mcp2515/CMakeLists.txt
pico_enable_stdio_uart(pico-mcp2515 1)
pico_enable_stdio_usb(pico-mcp2515 1)
- 修改 pico-mcp2515/include/mcp2515/mcp2515.h
根据我们上面的连接修改 SPI 的引脚
比如:
public:
MCP2515(
spi_inst_t* CHANNEL = spi0,
uint8_t CS_PIN = 5,
uint8_t TX_PIN = 3,
uint8_t RX_PIN = 4,
uint8_t SCK_PIN = 6,
uint32_t _SPI_CLOCK = DEFAULT_SPI_CLOCK
);
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/pico-mcp2515/src/pico-mcp2515.cpp
pico-mcp2515.cpp
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "mcp2515/mcp2515.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
int main() {
MCP2515 can0;
struct can_frame rx;
struct can_frame tx;
tx.can_id = 0x123;
tx.can_dlc = 8;
tx.data[0] = 0x11;
tx.data[1] = 0x22;
tx.data[2] = 0x33;
tx.data[3] = 0x44;
tx.data[4] = 0x55;
tx.data[5] = 0x66;
tx.data[6] = 0x77;
tx.data[7] = 0x88;
stdio_init_all();
//Initialize interface
can0.reset();
can0.setBitrate(CAN_1000KBPS, MCP_16MHZ);
can0.setLoopbackMode();
// loopback
while(true) {
MCP2515::ERROR result = can0.sendMessage(&tx);
if(result == MCP2515::ERROR_OK) {
printf("CAN TX: sent successfully ...\r\n");
}
sleep_ms(1000);
if(can0.readMessage(&rx) == MCP2515::ERROR_OK) {
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
printf("CAN RX: data[%d]: 0x%x\r\n", i, rx.data[i]);
}
}
sleep_ms(1000);
}
return 0;
}
-
编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
编译成功后, 在 pico-examples/build/pico-mcp2515/ 目录下会产生一个名为 pico-mcp2515.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
- 重启 RP2040
-
将 pico-mcp2515.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失
-
验证
打开串口 /dev/ttyS4, 我们能看到如下打印:
CAN TX: sent successfully ...
CAB RX: data[0]: 0x11
CAB RX: data[1]: 0x22;
CAB RX: data[2]: 0x33;
CAB RX: data[3]: 0x44;
CAB RX: data[4]: 0x55;
CAB RX: data[5]: 0x66;
CAB RX: data[6]: 0x77;
CAB RX: data[7]: 0x88;
PWM
1. 准备
- 一块 Radxa X4
- 一个 LED
2. 连接
| Radxa X4 | <--> | LED |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_5 | <--> | LED |
| PIN_1 | <--> | VCC |
| PIN_9 | <--> | GND |
这里的 PIN_5 对应 下面代码中的 GPIO29, 详细请参考 GPIO 定义
3. 测试
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/pwm/led_fade/pwm_led_fade.c
pwm_led_fade.c
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/time.h"
#include "hardware/irq.h"
#include "hardware/pwm.h"
#define PWD_FADE_LED_PIN 29
void on_pwm_wrap() {
static int fade = 0;
static bool going_up = true;
pwm_clear_irq(pwm_gpio_to_slice_num(PWD_FADE_LED_PIN));
if (going_up) {
++fade;
if (fade > 255) {
fade = 255;
going_up = false;
}
} else {
--fade;
if (fade < 0) {
fade = 0;
going_up = true;
}
}
pwm_set_gpio_level(PWD_FADE_LED_PIN, fade * fade);
}
int main() {
gpio_set_function(PWD_FADE_LED_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_PWM);
uint slice_num = pwm_gpio_to_slice_num(PWD_FADE_LED_PIN);
pwm_clear_irq(slice_num);
pwm_set_irq_enabled(slice_num, true);
irq_set_exclusive_handler(PWM_IRQ_WRAP, on_pwm_wrap);
irq_set_enabled(PWM_IRQ_WRAP, true);
pwm_config config = pwm_get_default_config();
pwm_config_set_clkdiv(&config, 4.f);
pwm_init(slice_num, &config, true);
while (1)
tight_loop_contents();
}
-
编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
编译成功后, 在 pico-examples/build/pwm/led_fade/ 目录下会产生一个名为 pwm_led_fade.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
- 重启 RP2040
-
将 pwm_led_fade.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失后, LED 会由暗到亮/由亮到暗渐变
PoE FAN
1. 准备
- 一块 Radxa X4
- 一个 瑞莎 25W PoE+ HAT X4 专用款
2. 连接
如图所示,将 瑞莎 25W PoE+ HAT X4 专用款 安装在 Radxa X4 上:
3. 测试
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/pio/onewire/onewire.c
onewire.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "pico/binary_info.h"
#include "onewire_library.h" // onewire library functions
#include "ow_rom.h" // onewire ROM command codes
#include "ds18b20.h" // ds18b20 function codes
#define FAN_PIN 13
#define TEMP_THRESHOLD 45.0
#define CONVERSION_DELAY_MS 750 // DS18B20 conversion time is about 750ms
#define SLEEP_BETWEEN_READS_MS 1000 // Delay between consecutive temperature reads
int main() {
stdio_init_all();
PIO pio = pio0;
uint gpio = 4;
// configure PIN 13
gpio_init(FAN_PIN);
gpio_set_dir(FAN_PIN, GPIO_OUT);
OW ow;
uint offset;
if (pio_can_add_program(pio, &onewire_program)) {
offset = pio_add_program(pio, &onewire_program);
if (ow_init(&ow, pio, offset, gpio)) {
int maxdevs = 10;
uint64_t romcode[maxdevs];
int num_devs = ow_romsearch(&ow, romcode, maxdevs, OW_SEARCH_ROM);
printf("Found %d devices\n", num_devs);
for (int i = 0; i < num_devs; i++) {
printf("\t%d: 0x%llx\n", i, romcode[i]);
}
while (true) {
// start temperature conversion in parallel on all devices
ow_reset(&ow);
ow_send(&ow, OW_SKIP_ROM);
ow_send(&ow, DS18B20_CONVERT_T);
// wait for the conversion to finish
sleep_ms(CONVERSION_DELAY_MS);
for (int i = 0; i < num_devs; i++) {
ow_reset(&ow);
ow_send(&ow, OW_MATCH_ROM);
for (int b = 0; b < 64; b += 8) {
ow_send(&ow, romcode[i] >> b);
}
ow_send(&ow, DS18B20_READ_SCRATCHPAD);
int16_t temp = ow_read(&ow) | (ow_read(&ow) << 8);
float temperature = temp / 16.0;
// set fan speed to max
if (temperature >= TEMP_THRESHOLD) {
printf("\tTemperature >= 45, Device %d: temp: %.2f\n", i, temperature);
gpio_put(FAN_PIN, 0);
} else {
// set fan speed to min
printf("\tTemperature < 45, Device %d: temp: %.2f\n", i, temperature);
gpio_put(FAN_PIN, 1);
}
}
// sleep between consecutive reads
sleep_ms(SLEEP_BETWEEN_READS_MS);
}
} else {
puts("could not initialise the driver");
}
} else {
puts("could not add the program");
}
return 0;
}
-
编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
成功编译后,在 pico-examples/build/pio/onewire/ 目录下会产生一个名为 pio_onwire.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
- 重启 RP2040
-
将 pio_onwire.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失后, 程序开始执行,如果 PoE 温度大于等于 45 摄氏度,风扇会全速转,否则风扇会停下
UART
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/uart/hello_uart/hello_uart.c
hello_uart.c
/**
* Copyright (c) 2020 Raspberry Pi (Trading) Ltd.
*
* SPDX-License-Identifier: BSD-3-Clause
*/
#include <stdio.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
/// \tag::hello_uart[]
#define UART_ID uart0
#define BAUD_RATE 115200
// We are using pins 0 and 1, but see the GPIO function select table in the
// datasheet for information on which other pins can be used.
#define UART_TX_PIN 0
#define UART_RX_PIN 1
int main() {
// Set up our UART with the required speed.
uart_init(UART_ID, BAUD_RATE);
// Set the TX and RX pins by using the function select on the GPIO
// Set datasheet for more information on function select
gpio_set_function(UART_TX_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_UART);
gpio_set_function(UART_RX_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_UART);
// Use some the various UART functions to send out data
// In a default system, printf will also output via the default UART
// Send out a character without any conversions
uart_putc_raw(UART_ID, 'A');
// Send out a character but do CR/LF conversions
uart_putc(UART_ID, 'B');
// Send out a string, with CR/LF conversions
while(1) {
uart_puts(UART_ID, "Hello, UART!\r\n");
sleep_ms(1000);
}
}
/// \end::hello_uart[]
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/uart/hello_uart/CMakeLists.txt
CMakeLists.txt
add_executable(hello_uart
hello_uart.c
)
# pull in common dependencies
target_link_libraries(hello_uart pico_stdlib)
# create map/bin/hex file etc.
pico_add_extra_outputs(hello_uart)
# add url via pico_set_program_url
example_auto_set_url(hello_uart)
pico_enable_stdio_usb(hello_uart 1)
pico_enable_stdio_uart(hello_uart 1)
-
编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
编译成功后, 在 pico-examples/build/uart/hello_uart/ 目录下会产生一个名为 hello_uart.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
- 重启 RP2040
-
将 hello_uart.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失后, 程序开始执行
-
终端输入以下命令,查看串口输出
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyS4 -b 115200
- 验证
在 minicom 中,你将看到终端每隔一秒输出一行 "Hello, UART!"
Intel CPU 通过 Uart 控制 RP2040
- PWM
- UART
风扇
本段示例旨在为用户提供一个 Radxa X4 CPU 与 MCU RP2040 通信的例子,通过获取 Radxa X4 CPU 的温度,当达到指定温度时,让风扇转起来。
1. 连接
将风扇的 pwm 引脚连接到 PIN_3, 风扇 VCC 连接 Radxa X4 的 VCC, 风扇 GND 连接 Radxa X4 的 GND
2. Radxa X4 安装所需要的 Python 库
pip install pyserial psutil
sudo apt-get update
sudo apt-get install stress
sudo apt-get install minicom
3. 在 Radxa X4 上新建一个 Temperature.py 的文件,内容如下:
Temperature.py
import psutil
import serial
import time
SERIAL_PORT = '/dev/ttyS0'
BAUD_RATE = 115200
set = serial.Serial(SERIAL_PORT, BAUD_RATE)
def get_cpu_temperature():
# get temperature from PC Host
temps = psutil.sensors_temperatures()
if 'coretemp' in temps:
cpu_temp = temps['coretemp'][0].current
return cpu_temp
else:
return None
try:
while True:
temp = get_cpu_temperature()
if temp is not None:
print(f"CPU Temperature: {temp}°C")
set.write(f"{temp}\n".encode())
else:
print("Unable to read temperature.")
time.sleep(1)
except KeyboardInterrupt:
set.close()
print("Program terminated.")
4. 在 pico-examples/pwm/CMakeLists.txt 里面添加一个 pwm_fan 的目录
关于 pico-examples 如何使用请参考上面 pico-sdk/pico-examples 部分
将 pico-example/pwm/CMakeLists.txt 替换称以下代码
CMakeLists.txt
if (TARGET hardware_pwm)
add_subdirectory_exclude_platforms(hello_pwm)
add_subdirectory_exclude_platforms(led_fade)
add_subdirectory_exclude_platforms(measure_duty_cycle)
add_subdirectory_exclude_platforms(pwm_fan)
else()
message("Skipping PWM examples as hardware_pwm is unavailable on this platform")
endif()
5. 在 pico-examples/pwm/pwm_fan/ 目录下新建一个 CMakeLists.txt, 内容如下:
CMakeLists.txt
add_executable(pwm_fan
pwm_fan.c
)
# pull in common dependencies and additional pwm hardware support
target_link_libraries(pwm_fan pico_stdlib hardware_pwm)
# create map/bin/hex file etc.
pico_add_extra_outputs(pwm_fan)
# add url via pico_set_program_url
example_auto_set_url(pwm_fan)
6. 在 pico-examples/pwm/pwm_fan/ 目录下新建一个 pwm_fan.c,内容如下:
pwm_fan.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
#include "hardware/pwm.h"
#define UART_ID uart0
#define BAUD_RATE 115200
#define UART_TX_PIN 0
#define UART_RX_PIN 1
#define FAN_PWM_PIN 28
#define TEMP_THRESHOLD 60.0
void set_pwm_duty_cycle(uint slice_num, uint channel, float duty_cycle) {
if (duty_cycle < 0.0f) duty_cycle = 0.0f;
if (duty_cycle > 100.0f) duty_cycle = 100.0f;
uint16_t level = (uint16_t)(duty_cycle * (float)(1 << 16) / 100.0f);
pwm_set_gpio_level(FAN_PWM_PIN, level);
}
int main() {
stdio_init_all();
uart_init(UART_ID, BAUD_RATE);
gpio_set_function(UART_TX_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_UART);
gpio_set_function(UART_RX_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_UART);
uart_set_format(UART_ID, 8, 1, UART_PARITY_NONE);
uart_set_fifo_enabled(UART_ID, false);
gpio_set_function(FAN_PWM_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_PWM);
uint slice_num = pwm_gpio_to_slice_num(FAN_PWM_PIN);
pwm_config config = pwm_get_default_config();
pwm_config_set_clkdiv(&config, 4.0f);
pwm_init(slice_num, &config, true);
char buffer[32];
int index = 0;
printf("Waiting for data...\n");
while (1) {
if (uart_is_readable(UART_ID)) {
char c = uart_getc(UART_ID);
if (c == '\n') {
buffer[index] = '\0';
float temperature = atof(buffer);
printf("Received temperature: %.2f°C\n", temperature);
if (temperature > TEMP_THRESHOLD) {
set_pwm_duty_cycle(slice_num, PWM_CHAN_A, 100.0f);
} else {
set_pwm_duty_cycle(slice_num, PWM_CHAN_A, 0.0f);
}
index = 0;
} else {
buffer[index++] = c;
if (index >= sizeof(buffer)) {
index = sizeof(buffer) - 1;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}
7. 编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
成功编译后,在 build/pwm/pwm_fan 目录下会产生一个名为 pwm_fan.uf2 的文件
8. 烧录
- 重启 RP2040
- 将 pwm_fan.uf2 文件拖入到 RP2040 中,待 RP2040 消失后, 程序开始读取 /dev/ttyS0 的消息
9. 板端运行 Temperature.py
sudo python3 Temperature.py
程序成功运行的话,该程序会获取 Radxa X4 当前温度,将温度发送到串口 /dev/ttyS0,并格式化输出温度,如 "CPU Temperature: 42.0°C"
10. 板端运行 minicom
sudo minicom -D /dev/ttyS0 -b 115200
查看 RP2040 是否有接收到来自 Radxa X4 发送的温度,若成功接收到, minicom 会输出相应温度,如: "Received temperature: 42.00°C"
该实例目的是通过 Intel CPU 去控制 RP2040 的 GPIO 资源,诠释 Intel CPU 与 RP2040 的 Uart 通信。
Intel CPU 通过 Uart 去控制 40-PIN 上的 GPIO
1. 准备
-
一块 Radxa X4
-
一个 LED
2. 连接
| Radxa X4 | <--> | LED |
|---|---|---|
| PIN_3 | <--> | LED |
| PIN_1 | <--> | VCC |
| PIN_9 | <--> | GND |
这里的 PIN_3 对应 下面代码中的 GPIO29, 详细请参考 GPIO 定义
3. 测试
- 将以下代码替换 pico-examples/uart/hello_uart/hello_uart.c
hello_uart.c
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "pico/stdlib.h"
#include "hardware/uart.h"
#define UART_ID uart0
#define BAUD_RATE 115200
#define UART_TX_PIN 0
#define UART_RX_PIN 1
#define BLINK_PIN 29
int main() {
gpio_init(BLINK_PIN);
gpio_set_dir(BLINK_PIN, GPIO_OUT);
uart_init(UART_ID, BAUD_RATE);
gpio_set_function(UART_TX_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_UART);
gpio_set_function(UART_RX_PIN, GPIO_FUNC_UART);
uart_set_hw_flow(UART_ID, false, false);
while(1) {
if(uart_is_readable(UART_ID)) {
uint8_t ch = uart_getc(UART_ID);
uart_puts(UART_ID, "Received data!\r\n");
uart_putc(UART_ID, ch);
gpio_put(BLINK_PIN, 1);
} else {
gpio_put(BLINK_PIN, 0);
uart_puts(UART_ID, "Uart is not readable!\r\n");
}
sleep_ms(500);
}
return 0;
}
-
编译
cd pico-examples/build
rm -rf *
cmake ..
make -j$(nproc)
编译成功后, 在 pico-examples/build/pwm/led_fade/ 目录下会产生一个名为 hello_uart.uf2 的文件
-
烧录
-
验证
-
打开终端, 向 /dev/ttyS4 发送字符串
-
RP2040 接收到字符串, Led 则亮起,否则 Led 不亮
-