interface-usage
Interface Usage Guidelines
Interface preview
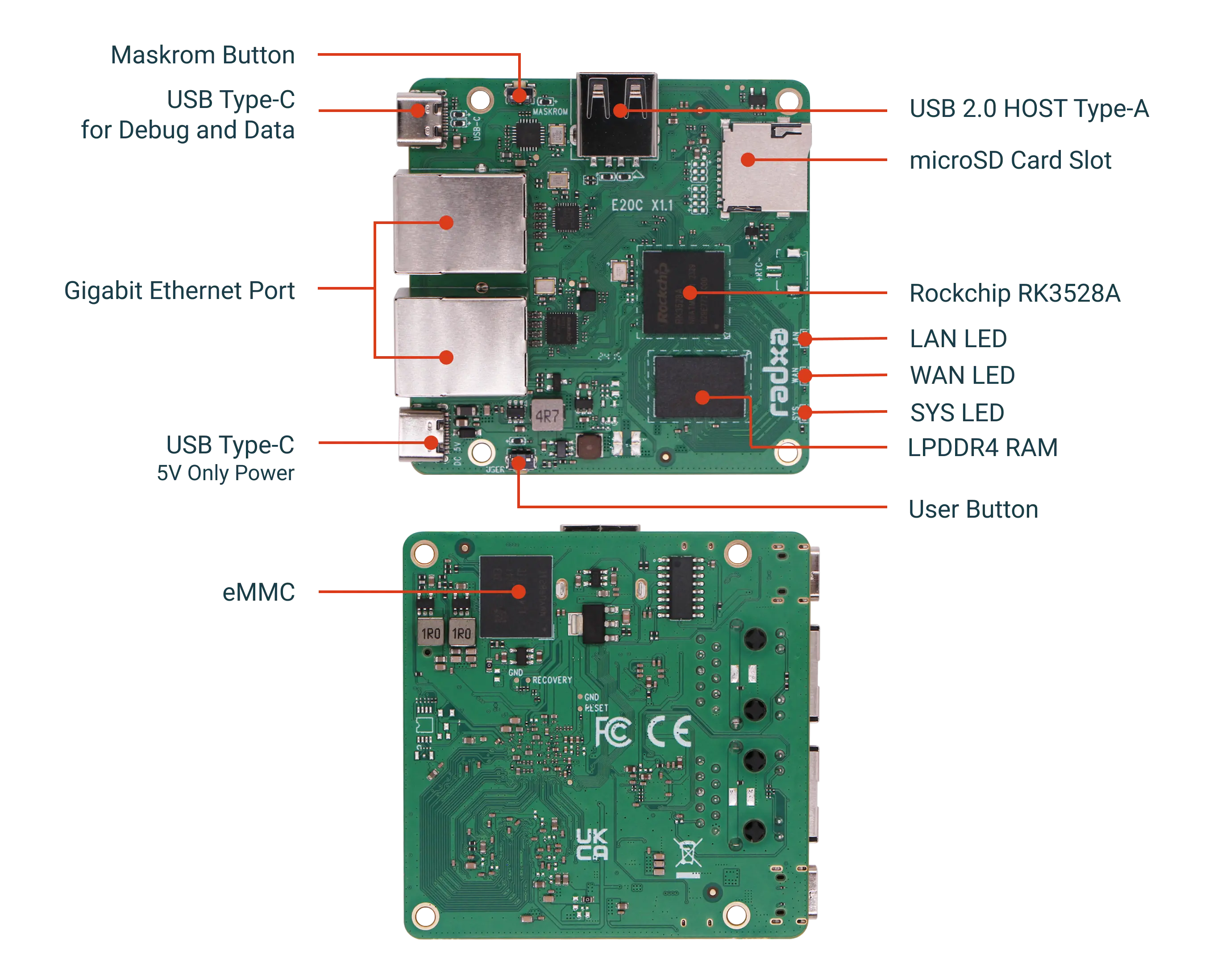
Interface Usage Notes
SYS LED
System status LED, will blink beat by beat when the system is booting up, green light.
WAN / LAN LED
The WAN/LAN LED follows the signal of the WAN/LAN port.
User Button
User button.
USB Type-C 5V Power Connector
Power input, Radxa E20C fixed voltage is 5V input, please refer to Power Supply .
Gigabit Ethernet Port
The Radxa E20C provides two Gigabit Ethernet ports. Under OpenWrt systems, these two ports can be flexibly configured as WAN (Wide Area Network Interface) or LAN (Local Area Network Interface) ports, providing users with a highly customised network solution.
Unique MAC Address
The MAC address of the Radxa E20C is unique and fixed. The MAC remains unchanged after every power or software reboot, and also after a re-flash.
Port Speed Test
- Install the iperf3 utility
sudo apt-get install iperf3
- Run the command on the server side:
iperf -s
- Test the speed
- Test upload speed
iperf3 -c server-ip -t 60
- Test download speed
iperf3 -c server-ip -t 60 -R
USB Type-C
As a debugging port, it is also a burning port to view logs and access the device, with a default baud rate of 1500000, as well as a TYPE-C port to complete the flashing.
Maskrom Button
Maskrom button to enter Maskrom mode to complete the flashing.
USB 2.0 Host
-
Repeatedly unplugging peripherals
Repeatedly plugging and unplugging USB peripherals ensures that they are recognised and used correctly every time.
Identifying storage devices
$ lsusb
Bus 001 Device 003: ID 067b:2731 Prolific Technology, Inc. USB SD Card Reader
As you can see above, the Micro-SD Card Reader has been successfully recognised here.
-
Transmission Rate
- Identify the USB memory device
Confirm the USB memory device with lsblk
$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
sda 8:0 1 29.3G 0 diskAs shown above, the USB storage device inserted into the Radxa E20C is /dev/sda.
- Read Test
$ sudo dd if=/dev/sda of=/dev/null bs=1M count=100 100+0 records in 100+0 records out 104857600 bytes (105 MB, 100 MiB) copied, 3.35508 s, 31.3 MB/s
This command will read data from the USB device and write it to /dev/null to test the read speed. The block size specified here is 1M, and 100 blocks are specified to be read, so a total of 100 MB of data is read, and the read speed is 31.3 MB/s.
- Write test
$ sudo dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/sda bs=1M count=100 100+0 records in 100+0 records out 104857600 bytes (105 MB, 100 MiB) copied, 5.12891 s, 20.4 MB/s
The block size specified here is 1M, 100 blocks were written, a total of 100M of data was written, and the write speed was 20.4 MB/s.
microSD Card Slot
Introduction
Micro SD, known as Micro Secure Digital, is a small memory card that is a variant of the Secure Digital (SD) card. It was developed and introduced by the SD Association to provide expandable storage solutions for portable devices.
eMMC
List Disk
$ lsblk
NAME MAJ:MIN RM SIZE RO TYPE MOUNTPOINT
mmcblk0 179:0 0 58G 0 disk
|-mmcblk0p1 179:1 0 16M 0 part /config
|-mmcblk0p2 179:2 0 300M 0 part /boot/efi
|-mmcblk0p3 179:3 0 57.6G 0 part /config
mmcblk1 179:32 0 14.6G 0 disk
mmcblk1boot0 179:64 0 4M 1 disk
mmcblk1boot1 179:96 0 4M 1 disk
zram0 254:0 0 1.9G 0 disk [SWAP]
``
mmcblk1 is the eMMC.
#### read test
```bash
# dd if=/dev/mmcblk1 of=/dev/null bs=64k count=16k
16384+0 records in
16384+0 records out
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 3.9136 s, 274 MB/s
``
Read speed 274 MB/s
#### Write test
```bash
# dd if=/dev/zero of=/dev/mmcblk1 bs=64k count=16k
16384+0 records in
16384+0 records out
1073741824 bytes (1.1 GB, 1.0 GiB) copied, 20.6661 s, 52.0 MB/s
``
Write speed: 52.0 MB/s