DeepLabv3 Example
This document introduces how to use the CIX P1 NPU SDK to convert DeepLabv3 into a model that can run on the CIX SOC NPU.
There are four main steps:
Steps 1-3 should be executed in an x86 Linux environment.
- Download the NPU SDK and install the NOE Compiler
- Download the model files (code and scripts)
- Compile the model
- Deploy the model to Orion O6
Download NPU SDK and Install NOE Compiler
Refer to Install NPU SDK for the installation of the NPU SDK and NOE Compiler.
Download Model Files
The CIX AI Model Hub includes all necessary files for DeepLabv3. Please follow the instructions in Download the CIX AI Model Hub Repository and navigate to the corresponding directory.
cd ai_model_hub/models/ComputeVision/Semantic_Segmentation/onnx_deeplab_v3
Please confirm that the directory structure is as shown below:
.
├── cfg
│ └── onnx_deeplab_v3_build.cfg
├── datasets
│ └── calibration_data.npy
├── graph.json
├── inference_npu.py
├── inference_onnx.py
├── ReadMe.md
├── test_data
│ └── ILSVRC2012_val_00004704.JPEG
└── Tutorials.ipynb
Compile the Model
Users do not need to compile the model from scratch, as Radxa provides a precompiled deeplab_v3.cix model (which can be downloaded using the steps below). If using the precompiled model, you can skip the "Compile the Model" step.
wget https://modelscope.cn/models/cix/ai_model_hub_24_Q4/resolve/master/models/ComputeVision/Semantic_Segmentation/onnx_deeplab_v3/deeplab_v3.cix
Prepare ONNX Model
-
Download the ONNX model
-
Simplify the model
Here we use
onnxsimfor input fixing and model simplification.pip3 install onnxsim onnxruntime
onnxsim deeplabv3_resnet50.onnx deeplabv3_resnet50-sim.onnx --overwrite-input-shape 1,3,520,520
Compile the Model
CIX SOC NPU supports INT8 computation. Before compiling the model, we need to use the NOE Compiler for INT8 quantization.
-
Prepare the calibration dataset
-
Use the existing calibration dataset from
datasets.
└── calibration_data.npy -
Prepare the calibration dataset yourself
The
test_datadirectory already contains multiple images for the calibration dataset..
├── 1.jpeg
└── 2.jpegRefer to the following script to generate the calibration file.
import sys
import os
import numpy as np
_abs_path = os.path.join(os.getcwd(), "../../../../")
sys.path.append(_abs_path)
from utils.image_process import preprocess_image_deeplabv3
from utils.tools import get_file_list
# Get a list of images from the provided path
images_path = "test_data"
images_list = get_file_list(images_path)
data = []
for image_path in images_list:
input = preprocess_image_deeplabv3(image_path)
data.append(input)
# concat the data and save calib dataset
data = np.concatenate(data, axis=0)
np.save("datasets/calib_data_tmp.npy", data)
print("Generate calib dataset success.")
-
-
Use the NOE Compiler to quantize and compile the model
-
Create a configuration file for quantization and compilation, refer to the following configuration:
[Common]
mode = build
[Parser]
model_type = onnx
model_name = deeplab_v3
detection_postprocess =
model_domain = image_segmentation
input_model = ./deeplabv3_resnet50-sim.onnx
input = input
input_shape = [1, 3, 520, 520]
output = output
output_dir = ./
[Optimizer]
output_dir = ./
calibration_data = ./datasets/calib_data_tmp.npy
calibration_batch_size = 1
metric_batch_size = 1
dataset = NumpyDataset
quantize_method_for_weight = per_channel_symmetric_restricted_range
quantize_method_for_activation = per_tensor_asymmetric
save_statistic_info = True
[GBuilder]
outputs = deeplab_v3.cix
target = X2_1204MP3
profile = True
tiling = fps -
Compile the model
tipIf you encounter a cixbuild error
[E] Optimizing model failed! CUDA error: no kernel image is available for execution on the device ..., it means the current version of torch does not support this GPU. Please completely uninstall the current version of torch and download the latest version from the official torch website.cixbuild ./onnx_deeplab_v3_build.cfg
-
Model Deployment
NPU Inference
Copy the compiled .cix model file to the Orion O6 development board for model verification.
python3 inference_npu.py --images ./test_data/ --model_path ./deeplab_v3.cix
(.venv) radxa@orion-o6:~/NOE/ai_model_hub/models/ComputeVision/Semantic_Segmentation/onnx_deeplab_v3$ time python3 inference_npu.py --images ./test_data/ --model_path ./deeplab_v3.cix
npu: noe_init_context success
npu: noe_load_graph success
Input tensor count is 1.
Output tensor count is 1.
npu: noe_create_job success
save output: noe_ILSVRC2012_val_00004704.JPEG
npu: noe_clean_job success
npu: noe_unload_graph success
npu: noe_deinit_context success
real 0m9.047s
user 0m4.314s
sys 0m0.478s
The results are saved in the output folder.
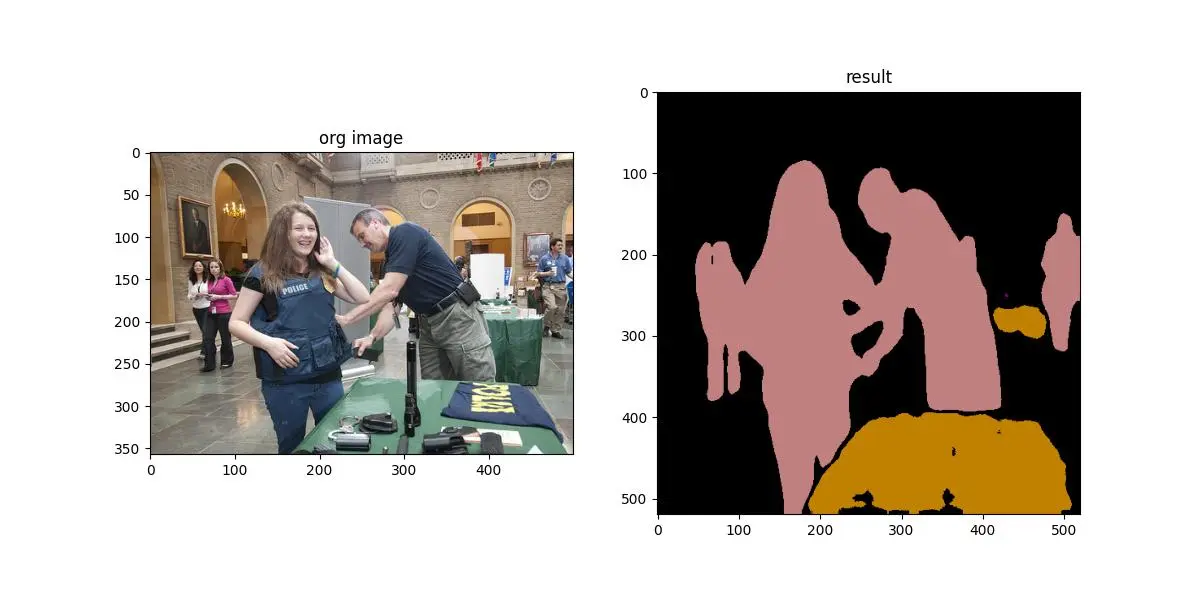
CPU Inference
Use the CPU for inference verification of the ONNX model. This can be run on an x86 host or on Orion O6.
python3 inference_onnx.py --images ./test_data/ --onnx_path ./deeplabv3_resnet50-sim.onnx
(.venv) radxa@orion-o6:~/NOE/ai_model_hub/models/ComputeVision/Semantic_Segmentation/onnx_deeplab_v3$ time python3 inference_onnx.py --images ./test_data/ --onnx_path ./deeplabv3_resnet50-sim.onnx
save output: onnx_ILSVRC2012_val_00004704.JPEG
real 0m7.605s
user 0m33.235s
sys 0m0.558s
The results are saved in the output folder.
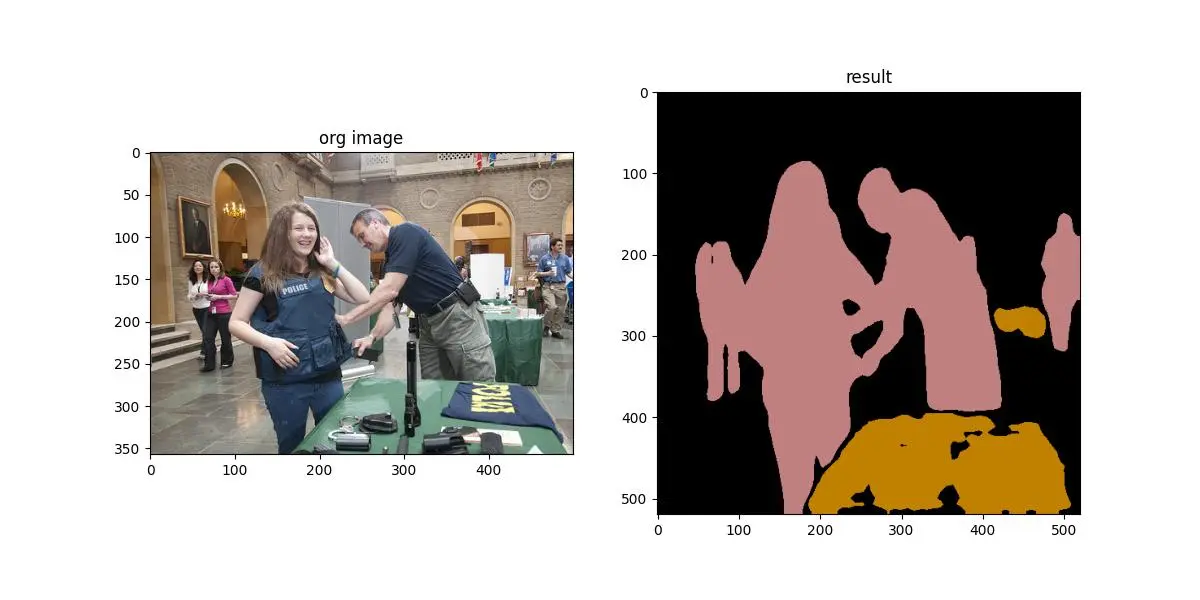
It can be seen that the inference results on both NPU and CPU are consistent, but the running speed is significantly reduced.
Reference Document
Paper link: Rethinking Atrous Convolution for Semantic Image Segmentation