Remote Access
SSH
This is a tutorial on how to access the board remotely from another computer using SSH.
View username
Open a terminal on the board and enter the following command in the terminal to view the username
radxa@undefined:~$ whoami radxa
This command displays the username of the current user, as shown above, the current user's username is radxa
View IP address
View IP by command
Open a terminal on the board and enter the following command in the terminal to view the IP address:
radxa@undefined:~$ ip a
The ip address on the same network segment as the host is the ip address we need for SSH connection, e.g. 192.168.2.100 in the following output is the ip address we need.
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00:00
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
inet6 ::1/128 scope host
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
2: eth0: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc mq state UP group default qlen 1000
link/ether 56:ae:03:82:18:51 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
inet 192.168.2.100/24 brd 192.168.2.255 scope global dynamic noprefixroute eth0
valid_lft 43176sec preferred_lft 43176sec
inet6 fe80::8e:d164:96ea:40b6/64 scope link noprefixroute
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
Finding IPs with Angryip
This method can be used to look up an ip address when you can't operate the motherboard directly to get an ip address without a screen or remotely.
-
First the host PC needs to download Angryip, then make sure the host PC and the board are on the same LAN.
-
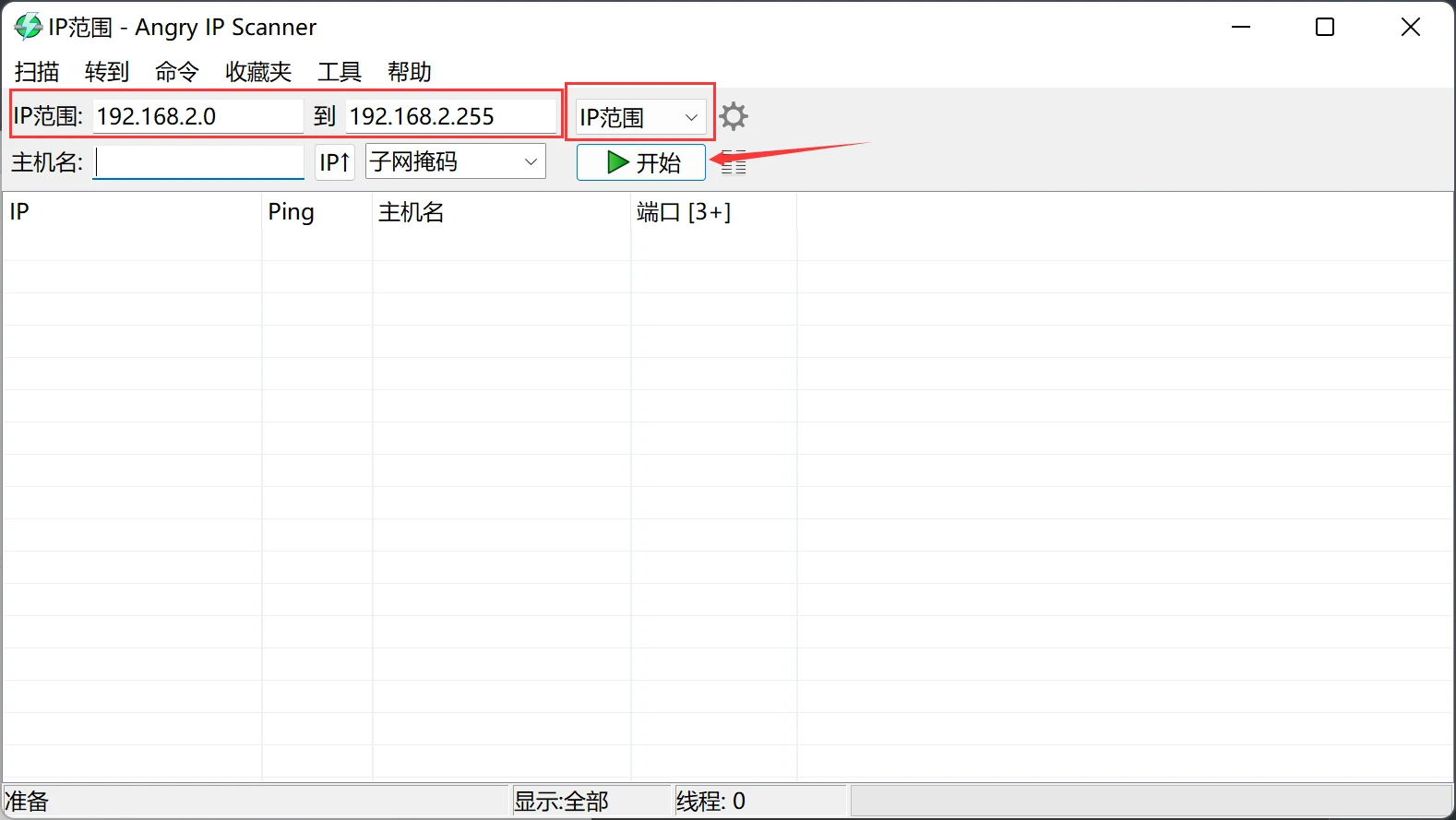
Open Angryip, select the IP range from 192.168.2.0 - 192.168.2.255 (select the network segment where the host PC and the motherboard are located), click Start, as shown in the figure.
-
-
Ctrl + F Look for the
rockkeyword to find the IP address of the board.
Checking SSH Service Status
Run the following command in a terminal:
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo systemctl status ssh
This command is used to view the status of the SSH service. If you run this command and are prompted with "Unit ssh.service could not be found.", then you need to install the SSH service.
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt-get update radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt-get install openssh-server openssh-sftp-server
● ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server
Loaded: loaded (/lib/systemd/system/ssh.service; enabled; preset: enabled)
Active: active (running) since Wed 2024-05-08 07:52:50 UTC; 24min ago
TriggeredBy: ● ssh.socket
Docs: man:sshd(8)
man:sshd_config(5)
Process: 637 ExecStartPre=/usr/sbin/sshd -t (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Main PID: 657 (sshd)
Tasks: 1 (limit: 3420)
Memory: 5.5M
CPU: 398ms
CGroup: /system.slice/ssh.service
└─657 "sshd: /usr/sbin/sshd -D [listener] 0 of 10-100 startups"
May 08 07:52:49 radxa-zero systemd[1]: Starting ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server...
May 08 07:52:50 radxa-zero sshd[657]: Server listening on :: port 22.
May 08 07:52:50 radxa-zero systemd[1]: Started ssh.service - OpenBSD Secure Shell server.
May 08 07:53:22 radxa-zero sshd[783]: Accepted password for radxa from 192.168.31.1 port 49474 ssh2
May 08 07:53:22 radxa-zero sshd[783]: pam_unix(sshd:session): session opened for user radxa(uid=1000) by (uid=0)
May 08 07:53:22 radxa-zero sshd[783]: pam_env(sshd:session): deprecated reading of user environment enabled
- If the status of
Activeisactive (running), the state of SSH is running. - If the status of
Activeisinactive (dead), then SSH is stopped, i.e. the service is not running and needs to be restarted.
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo systemctl restart ssh
- If you need to start the SSH service automatically at boot, please run the following command:
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo systemctl enable --now ssh
SSH connection to the board
ssh [username]@[IP address] # or ssh [username]@[hostname]
VNC
This is a tutorial on how to remotely access your system from a Windows computer using VNC.
Installing VNC Server
- Open the Terminal application and enter the following command to update the package list.
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt-get update
- Install TigerVNC Server by entering the following command.
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt-get install tigervnc-standalone-server
- Install the dbus-x11 dependency to ensure proper connection to your VNC server:
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt-get install dbus-x11
- After installation to complete the initial configuration of your VNC server, use the vncserver command to set the security password and create the initial configuration file:
radxa@undefined:~$ vncserver
Would you like to enter a view-only password (y/n)? n Prompt for view-only, would you like to select no and enter n so that you can operate remotely instead of just watching, depending on your situation?
Configuring the VNC Server
- Once TigerVNC starts, it will create a VNC session containing the IP address and port number (usually 5901) of the VNC server. To change the way the VNC server is configured, first stop the instance of the VNC server running on port 5901 with the following command:
radxa@undefined:~$ vncserver -kill :1
- When you run the vncserver command, an xstartup is generated in the ~/.vnc directory. If it is not generated, please create it manually and give it executable permissions:
radxa@undefined:~$ touch ~/.vnc/xstartup radxa@undefined:~$ chmod +x ~/.vnc/xstartup
Edit the xstartup configuration file as follows:
radxa@undefined:~$ cat ~/.vnc/xstartup #!/bin/sh unset SESSION_MANAGER unset DBUS_SESSION_BUS_ADDRESS unset XDG_RUNTIME_DIR /etc/X11/xinit/xinitrc [ -x /etc/vnc/xstartup ] && exec /etc/vnc/xstartup [ -r $HOME/.Xresources ] && xrdb $HOME/.Xresources xsetroot -solid grey #vncconfig -iconic & startkde &
- Once the configuration is edited, restart the VNC server:
radxa@undefined:~$ vncserver -localhost no
- View the VNC server:
radxa@undefined:~$ vncserver -list TigerVNC server sessions: X DISPLAY # RFB PORT # PROCESS ID SERVER :1 5901 2160 Xtigervnc :2 5902 2872 Xtigervnc
- Test the connection on the VNC viewer: On your Windows PC, open the VNC viewer, enter the IP address and port number of your product, and then authenticate with the VNC server's username and password.
Installing the VNC Viewer on a Windows PC
- Go to the VNC viewer download page on your web browser, e.g. https://www.realvnc.com/en/connect/download/viewer/
- Download and install the VNC viewer.
Connection Setup
- On the VNC viewer, enter the IP address and port number of the product. 2.
- Use the VNC server's user name and password to authenticate.
- After a successful connection, you can remote control.
TeamViewer
Installing TeamViewer
radxa@undefined:~$ wget https://download.teamviewer.com/download/linux/teamviewer-host_arm64.deb radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt install . /teamviewer-host_arm64.deb
configure TeamViewer
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo teamviewer setup # Agree to protocol login and authorization
uninstall xfce4-screensaver
This procedure fixes a problem with TeamViewer's keyboard and mouse controls not working due to prolonged hang time.
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt remove xfce4-screensaver
Configuring virtual monitors
This step is optional if a real monitor is connected.
radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt update radxa@undefined:~$ sudo apt install xserver-xorg-video-dummy radxa@undefined:~$ sudo mv /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-modesetting.conf /usr/share/X11/xorg.conf.d/20-modesetting.bak radxa@undefined:~$ sudo nano /etc/X11/xorg.conf.d/10-headless.conf
# Add the following and reboot
Section "Monitor"
Identifier "dummy_monitor"
HorizSync 28.0-80.0
VertRefresh 48.0-75.0
Modeline "1920x1080" 172.80 1920 2040 2248 2576 1080 1081 1084 1118
EndSection
Section "Device"
Identifier "dummy_card"
VideoRam 256000
Driver "dummy"
EndSection
Section "Screen"
Identifier "dummy_screen"
Device "dummy_card"
Monitor "dummy_monitor"
SubSection "Display"
EndSubSection
EndSection
Connecting to TeamViewer
You can refer to TeamViewer official documentation.